|
 |
- Search
| Clin Exp Reprod Med > Volume 39(2); 2012 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Lin28 has been known to control the proliferation and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. The purpose of this study was to determine the downstream effectors of Lin28 in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) by RNA interference and microarray analysis.
Methods
The control siRNA and Lin28 siRNA (Dharmacon) were transfected into mESCs. Total RNA was prepared from each type of transfected mESC and subjected to reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis to confirm the downregulation of Lin28. The RNAs were labeled and hybridized with an Affymetrix Gene-Chip Mouse Genome 430 2.0 array. The data analysis was accomplished by GenPlex 3.0 software. The expression levels of selected genes were confirmed by quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
Results
According to the statistical analysis of the cDNA microarray, a total of 500 genes were altered in Lin28-downregulated mESCs (up-regulated, 384; down-regulated, 116). After differentially expressed gene filtering, 31 genes were selected as candidate genes regulated by Lin28 downregulation. Among them, neuropeptide Y5 receptor and oocyte-specific homeobox 5 genes were significantly upregulated in Lin28-downregulated mESCs. We also showed that the families of neuropeptide Y receptor (Npyr) and oocyte-specific homeobox (Obox) genes were upregulated by downregulation of Lin28.
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) derived from the inner cell mass of blastocyst-stage embryos have two essential abilities, self-renewal and pluripotency [1]. Self-renewal allows them to persist in an environment preventing their differentiation, and pluripotency enables them to differentiate and form all three embryonic germ layers. Studies have been performed on the control mechanisms of such capabilities of ESCs, and it has been found that four genes-Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc-are responsible for making the induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells when the genes are overexpressed in somatic cells [2-4]. The iPS cells have been shown to be pluripotent and similar to ESCs, both in their markers and in their gene expression. In addition, other genes, Lin28 and Nanog, were also shown to facilitate the derivation of iPS cell formation in combination with Oct4 and Sox2 [3,5].
Lin28 is an RNA binding protein and originally identified as a heterochronic gene in controlling the developmental timing of Caenorhabditis elegans [6]. However, the molecular mechanism by which Lin28 controls developmental timing is still unclear. In mammals, Lin28 is widely expressed in early-stage embryos, with expression decreasing and becoming restricted to a few tissues such as skeletal and cardiac muscles [7]. In human tissues, Lin28 has been detected in normal ovarian surface epithelium and in mature oocytes [8]. In human and mouse ESCs, in particular, Lin28 is abundantly expressed and decreases dramatically upon induction of differentiation [9,10], and Lin28 is involved in the cell proliferation and facilitates the expression of Oct4 at the post-transcriptional level [11,12].
The biological significance of Lin28 is spotlighted by its capability to enhance the reprogramming of fibroblasts to iPS cells by the replacement of other factors such as Klf4 and c-Myc [3]. In addition, Lin28 is specifically activated in the subset of tumors that are poorly differentiated and associated with the worst prognosis [13]. Lin28 is predominantly located in the cytoplasm and plays roles in the regulation of gene expression in normal tissues and cancers. Lin28 has been suggested to be a post-transcriptional regulator by its RNA binding ability and has been shown to block let-7 microRNA (miRNA) processing by binding the loop of miRNA [14,15]. Therefore, Lin28 has an ability to promote reprogramming and maintain the self-renewal of ESCs by preventing production of mature let-7 miRNAs [16]. Also, this mechanism has been implicated in the aggressiveness of many different tumors by activating Lin28 protein [13]. Lin28 has also been reported to bind a specific subset of mRNAs and modulate their expression in addition to blocking the let-7 miRNA processing [17].
Based on the fact that Lin28 plays pleiotropic roles in the regulation of gene expression, in this study, we determined the downstream effectors regulated by Lin28 in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) using RNA interference (RNAi) and microarray analysis. We identified a list of Lin28-regulated genes. Among the genes on the list, we focused on neuropeptide Y5 receptor (Npy5r) and oocyte-specific homeobox 5 (Obox5) genes because of their relationship with ESCs based on previous reports and found the family members of Npyr and Obox genes also upregulated by Lin28 downregulation in mESCs.
J1 mESCs (SCRC-1010) were purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were maintained in a feeder-free condition on 0.1% gelatin-coated plates. The culture medium consisted of Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), 1% nonessential amino acids (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA), 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 g/mL streptomycin, 2 mM glutamine (Gibco Invitrogen) and 1,000 U/mL leukemia inhibitory factor (Chemicon, Temecula, CA, USA).
Lin28 siRNA (L-051530-01, Dharmacon, Denver, CO, USA) and control siRNA (D-001810-01-05, Dharmacon) were purchased. This siRNA was transfected into J1 cells with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, a total of 5├Ś105 cells were plated in 6-well plates and transfected using 200 pmol siRNA and 10 ┬ĄL of Lipofectamine 2000 per well. After 5 hours of incubation, 2 mL of growth medium was added to the cells. The next day, the medium was replaced with fresh growth medium. Following 24 hours of incubation, the cells were harvested for analysis.
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol (Invitrogen) and biotinylated cRNA were prepared from 3 ┬Ąg of total RNA using an RNA amplification kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA) following the manufacturer's instructions. Following fragmentation, 12 ┬Ąg of cRNA was hybridized to the Affymatrix Genechip Mouse Genome 430 2.0 array (Affymatrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The arrays were scanned by using a GeneChip scanner 3000 7 G (Affymatrix) and array data analysis was performed using GenPlex 3.0 software (Istech Co., Goyang, Korea).
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol (Invitrogen) and 2 ┬Ąg of total RNA was used for the first cDNA synthesis using moloney murine leukemia virus (MMLV) reverse transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using the iQ SYBR Green Supermix PCR reagent (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Reactions were carried out using iCycler (Bio-Rad) and the results were evaluated with the iCycler real-time detection system software. For quantitation, the target genes were normalized against the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) gene and performed by determining the cycle threshold value (CT). Relative quantitation of target gene expression was evaluated by the comparative CT method. The PCR primers used in this study are listed in Table 1.
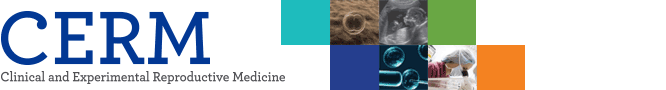
To determine the downstream effectors controlled by Lin28 in mESCs, we first performed cellular knockdown of Lin28 by RNAi. The control siRNA and Lin28 siRNA were transfected into mESCs and the expression of Lin28 was analyzed by RT-PCR. It was shown that the expression of Lin28 was effectively suppressed compared to the control siRNA transfected cells (Figure 1A). Using the total RNA from three sets of independently prepared cells, we performed microarray analysis to compare the gene expression profiles of the control and Lin28 knocked down mESCs. A heat map and scatter plot of the cDNA microarray depicts the high correlation between the control and experimental samples as well as the up- and down-regulated genes from microarray analysis (Figure 1B).
Among all of the genes, 500 genes were determined to be changed at least 2-fold in the Lin28 knocked down mESCs (up-regulated, 384; down-regulated, 116). According to the Affymatrix microarray guideline, we applied MAS5 detection filtering for selection of differentially expressed gene. After the filtering procedure, we finally selected 31 genes (up-regulated, 24; down-regulated, 7). We omitted some genes due to insufficient gene information and the rest of the genes (up-regulated, 19; down-regulated, 5) are listed in Table 2. Preliminarily, we examined the ordinary expression level of each selected gene in the mESCs (data not shown), and we performed RT-PCR analysis of the candidate genes using the cDNA from the control and Lin28-downregulated mESCs to confirm the microarray results (Figure 2). We found that the expressions of several genes, Mm.226989, Npy5r, Pfkfb2, Mm.150234, Zfp386, and Obox5 were significantly upregulated (Figure 2A), while Phactr2 was downregulated (Figure 2B) in Lin28 knocked down mESCs.
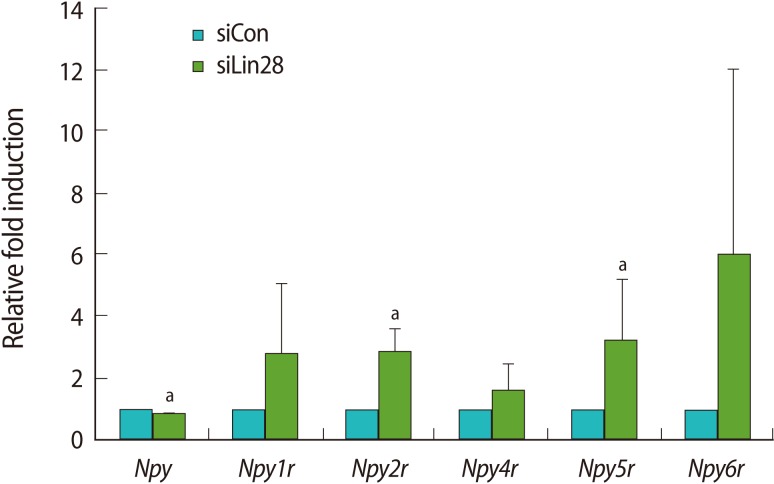
We focused on Npyr and Obox genes since their expression in ESCs was previously reported. Npy, one of the most abundant neuropeptides in the brain, exerts its functions by binding to six NPY receptors (Y1 to Y6) [18]. Mammals have five subtypes of NPY receptors, Y1 (Npy1r), Y2 (Npy2r), Y4 (Npy4r), Y5 (Npy5r), and Y6 (Npy6r). Thus, we examined the expression profiles of Npy and its receptors by quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis using the cDNA of the control and Lin28 knocked down mESCs (Figure 3). The results showed that Npy2r and Npy5r were significantly upregulated even though their basal expression levels were relatively low in mESCs. The results of other receptors, Npy1r, Npy4r, and Npy6r, showed the tendency of increasing level of expression. However, the expression of Npy itself was slightly, but significantly downregulated in the Lin28 knocked down mESCs.
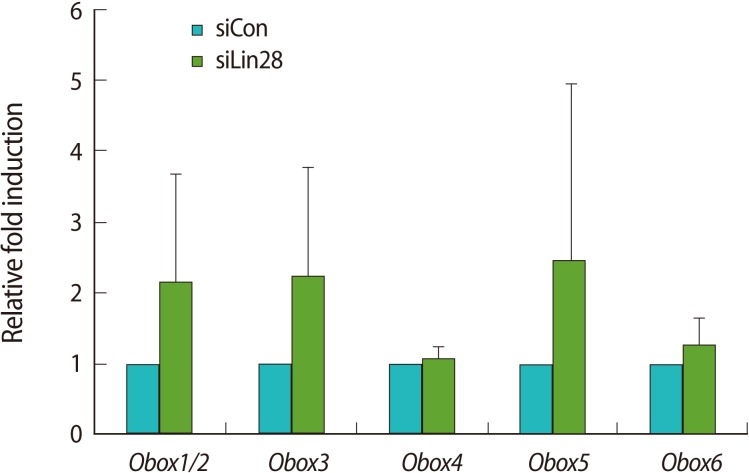
The Obox family consists of 6 members and is exclusively expressed in the ovary and testes [19-21]. Kim et al. [22] reported that the Obox family is expressed in mESCs and Obox4 regulates histone family gene expression. Thus, we examined the expression level of each Obox family gene in the Lin28 knocked down mESCs in comparison with the control mESCs by quantitative real-time RT-PCR (Figure 4). The results showed that the expression levels of Obox1/2, Obox3, Obox5, and Obox6 tended toward upregulation although the statistical significance value was low. Interestingly, however, the expression of Obox4 was not much changed in the Lin28 knocked down mESCs.
Lin28 is spotlighted by its ability to promote iPS cell production from somatic cells. It is abundantly expressed in ESCs and plays crucial roles in proliferation and self-renewal of ESCs. A major role of Lin28 in ESCs is to support the rapid growth of cells. However, the evidence used to explain the role of Lin28 in ESCs is controversial. Several reports have suggested that Lin28 facilitates cell proliferation by binding a subset of mRNA involved in the cell cycle and metabolism [11,12,23]. However, Darr and Benvenisty [10] reported that downregulation of Lin28 did not lead to differentiation, but rather Lin28 overexpression impaired the ability of cells to grow at clonal densities. Also, like other reprogramming factors, Lin28 has been reported to play a role in controlling the aggressiveness, recurrence, and metastasis of cancers [24-27]. Therefore, it is necessary to confine the corresponding downstream effectors of Lin28 in various cell types, including stem cells. In this study, we performed microarray analysis using the total RNA from transiently Lin28 knocked down mESCs by RNAi, and found that Npyr and Obox family members showed a tendency toward upregulation by Lin28 RNAi (Figures 3, 4).
The growth factor properties of NPY were demonstrated in various cell types including neurons, endothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and adipocyte precursor cells [28-31]. In the case of ESCs, it has been reported that NPY and its receptors are involved in maintaining the self-renewal and proliferation of hESCs [32]. NPY supports the long-term growth of undifferentiated hESCs in the feeder-free condition and both Y1 and Y5 receptors are involved in the NPY-mediated activation. Npy1r plays an important role in the regulation of mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation [33]. Through the Y1 receptor, NPY directly inhibits the differentiation of mesencymal progenitor cells. Therefore, since Npy and its receptor family are expressed in ESCs, it would be possible that Lin28 regulates the Npyr family to control the proliferation of mESCs. We could not, however, rule out the possibility that the upregulation of the Npyr family by Lin28 RNAi is through indirect regulation.
The Obox gene family has been known to be exclusively expressed in germ cells. Given the many similarities between germ cells and ESCs, sets of genes may express in both germ cells and ESCs. The expression of the Obox family is detected in mESCs as well as in oocytes [21,22]. Basically, Obox4 has been known to regulate the cAMP-dependent signaling cascades that maintain the intact germinal vesicle membrane of oocytes [21]. It has been suggested that Obox4 plays the following role in mESCs: Obox4 expression leads mESCs into a differentiated state with decreased expression levels of Oct4 and Sox2 [22]. This report also suggested that Obox4 might have a different role in mESCs than do other Obox family members such as Obox6. Interestingly, Obox4 is expressed as an unspliced transcript in mESCs, and the unspliced intron is spliced out upon the differentiation of mESCs [22]. Therefore, it is presumed that Obox family members other than Obox4 have a regulatory role in undifferentiated mESCs. In this study, we found that the Obox gene family, other than Obox4, had a tendency toward upregulation in mESCs by Lin28 RNAi. Thus, we propose that Lin28 might regulate the expression of the Obox family genes selectively to control the differentiation of mESCs in a fine-tuned manner.
Lin28 has been known to be an RNA-binding protein and function as a post-transcriptional regulator [9-12]. Our results showed that Lin28 also regulated the downstream effectors, Npyr and Obox family genes, functioning in the control of cell destination at the transcriptional level. Until now, it has not been clearly revealed how the expression of the genes, such as Npyr and Obox families, in ESCs is regulated. Thus, our results could also provide an important clue for the understanding of the regulation mechanism of gene expression in ESCs. Further elucidation of the other target genes of Lin28 in ESCs is needed for understanding the multiple functions of Lin28 in ESCs.
Notes
References
1. Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998;282:1145-1147.PMID: 9804556.


2. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006;126:663-676.PMID: 16904174.


3. Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007;318:1917-1920.PMID: 18029452.


4. Lowry WE, Richter L, Yachechko R, Pyle AD, Tchieu J, Sridharan R, et al. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:2883-2888.PMID: 18287077.



5. Darr H, Mayshar Y, Benvenisty N. Overexpression of NANOG in human ES cells enables feeder-free growth while inducing primitive ectoderm features. Development 2006;133:1193-1201.PMID: 16501172.


6. Moss EG, Lee RC, Ambros V. The cold shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C. elegans and is regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell 1997;88:637-646.PMID: 9054503.


7. Yang DH, Moss EG. Temporally regulated expression of Lin-28 in diverse tissues of the developing mouse. Gene Expr Patterns 2003;3:719-726.PMID: 14643679.


8. Assou S, Cerecedo D, Tondeur S, Pantesco V, Hovatta O, Klein B, et al. A gene expression signature shared by human mature oocytes and embryonic stem cells. BMC Genomics 2009;10:10PMID: 19128516.



9. Richards M, Tan SP, Tan JH, Chan WK, Bongso A. The transcriptome profile of human embryonic stem cells as defined by SAGE. Stem Cells 2004;22:51-64.PMID: 14688391.


10. Darr H, Benvenisty N. Genetic analysis of the role of the reprogramming gene LIN-28 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2009;27:352-362.PMID: 19038789.


11. Xu B, Zhang K, Huang Y. Lin28 modulates cell growth and associates with a subset of cell cycle regulator mRNAs in mouse embryonic stem cells. RNA 2009;15:357-361.PMID: 19147696.



12. Qiu C, Ma Y, Wang J, Peng S, Huang Y. Lin28-mediated post-transcriptional regulation of Oct4 expression in human embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2010;38:1240-1248.PMID: 19966271.


13. Viswanathan SR, Powers JT, Einhorn W, Hoshida Y, Ng TL, Toffanin S, et al. Lin28 promotes transformation and is associated with advanced human malignancies. Nat Genet 2009;41:843-848.PMID: 19483683.



14. Viswanathan SR, Daley GQ, Gregory RI. Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science 2008;320:97-100.PMID: 18292307.



15. Heo I, Joo C, Kim YK, Ha M, Yoon MJ, Cho J, et al. TUT4 in concert with Lin28 suppresses microRNA biogenesis through pre-microRNA uridylation. Cell 2009;138:696-708.PMID: 19703396.


16. Thomson JM, Newman M, Parker JS, Morin-Kensicki EM, Wright T, Hammond SM. Extensive post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications for cancer. Genes Dev 2006;20:2202-2207.PMID: 16882971.



17. Polesskaya A, Cuvellier S, Naguibneva I, Duquet A, Moss EG, Harel-Bellan A. Lin-28 binds IGF-2 mRNA and participates in skeletal myogenesis by increasing translation efficiency. Genes Dev 2007;21:1125-1138.PMID: 17473174.



18. Inui A. Neuropeptide Y feeding receptors: are multiple subtypes involved? Trends Pharmacol Sci 1999;20:43-46.PMID: 10101961.


19. Rajkovic A, Yan C, Yan W, Klysik M, Matzuk MM. Obox, a family of homeobox genes preferentially expressed in germ cells. Genomics 2002;79:711-717.PMID: 11991721.


20. Cheng WC, Hsieh-Li HM, Yeh YJ, Li H. Mice lacking the Obox6 homeobox gene undergo normal early embryonic development and are fertile. Dev Dyn 2007;236:2636-2642.PMID: 17676645.


21. Lee HS, Kim EY, Kim KH, Moon J, Park KS, Kim KS, et al. Obox4 critically regulates cAMP-dependent meiotic arrest and MI-MII transition in oocytes. FASEB J 2010;24:2314-2324.PMID: 20154267.


22. Kim HM, Ahn HJ, Lee HS, Lee KA, Lee SM, Kim HH, et al. Obox4 regulates the expression of histone family genes and promotes differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. FEBS Lett 2010;584:605-611.PMID: 20004198.


23. Peng S, Chen LL, Lei XX, Yang L, Lin H, Carmichael GG, et al. Genome-wide studies reveal that Lin28 enhances the translation of genes important for growth and survival of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2011;29:496-504.PMID: 21425412.


24. Peng S, Maihle NJ, Huang Y. Pluripotency factors Lin28 and Oct4 identify a sub-population of stem cell-like cells in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2010;29:2153-2159.PMID: 20101213.


25. Xue D, Peng Y, Wang F, Allan RW, Cao D. RNA-binding protein LIN28 is a sensitive marker of ovarian primitive germ cell tumours. Histopathology 2011;59:452-459.PMID: 22034885.


26. Hamano R, Miyata H, Yamasaki M, Sugimura K, Tanaka K, Kurokawa Y, et al. High expression of Lin28 is associated with tumour aggressiveness and poor prognosis of patients in oesophagus cancer. Br J Cancer 2012;106:1415-1423.PMID: 22433967.



27. King CE, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A, Sepulveda AR, Lee JS, Rustgi AK. LIN28B promotes colon cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Res 2011;71:4260-4268.PMID: 21512136.



28. Hansel DE, Eipper BA, Ronnett GV. Neuropeptide Y functions as a neuroproliferative factor. Nature 2001;410:940-944.PMID: 11309620.


29. Zukowska-Grojec Z, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, Rose W, Rone J, Movafagh S, Ji H, et al. Neuropeptide Y: a novel angiogenic factor from the sympathetic nerves and endothelium. Circ Res 1998;83:187-195.PMID: 9686758.


30. Pons J, Kitlinska J, Jacques D, Perreault C, Nader M, Everhart L, et al. Interactions of multiple signaling pathways in neuropeptide Y-mediated bimodal vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2008;86:438-448.PMID: 18641693.



31. Yang K, Guan H, Arany E, Hill DJ, Cao X. Neuropeptide Y is produced in visceral adipose tissue and promotes proliferation of adipocyte precursor cells via the Y1 receptor. FASEB J 2008;22:2452-2464.PMID: 18323405.


32. Son MY, Kim MJ, Yu K, Koo DB, Cho YS. Involvement of neuropeptide Y and its Y1 and Y5 receptors in maintaining self-renewal and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells. J Cell Mol Med 2011;15:152-165.PMID: 19874423.


33. Lee NJ, Doyle KL, Sainsbury A, Enriquez RF, Hort YJ, Riepler SJ, et al. Critical role for Y1 receptors in mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation and osteoblast activity. J Bone Miner Res 2010;25:1736-1747.PMID: 20200977.


Figure┬Ā1
Microarray analysis of Lin28 knocked down mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) by RNAi. (A) Control and Lin28 siRNA were transfected into J1 mESCs. Suppressed expression of Lin28 was shown after reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Two microphotographs representative of the results are shown. Gapdh was used as a loading control. (B) Affymatrix GeneChip mouse genome 430 arrays were used to evaluate the genome-wide expression of Lin28 knocked down mESCs. A heat map with hierarchical clustering (left panel) shows the results of the 500 selected genes after three independent microarray analyses. Scatter plots (right panel) comparing the expression pattern between the control and Lin28 knocked down mESCs show the up- and down-regulated genes from the microarray. siCon, control siRNA transfected; siLin28, Lin 28 siRNA transfected.
Figure┬Ā2
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of the selected genes after microarray analysis of the Lin28 knocked down mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). The expression of target genes selected by statistical method and filtering procedure after microarray analysis was examined by RT-PCR using specific primers with cDNA from control and Lin28 knocked down mESCs. Microphotographs representative of the results of (A) up-regulated and (B) down-regulated genes after RT-PCR are shown. Gapdh was used as a loading control. siCon, control siRNA transfected; siLin28, Lin28 siRNA transfected.

Figure┬Ā3
Upregulation of the Npyr family in Lin28 knocked down mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Relative expression of Npy and Npyr in Lin28 knocked down mESCs was confirmed by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The expression levels were calculated by computed tomography values, and the relative fold change was determined to compare the values of control mESCs. The data are represented as the mean┬▒SD from 3 independent experiments. The alphabet a represents statistical significance at p<0.05. siCon, control siRNA transfected; siLin28, Lin28 siRNA transfected.
Figure┬Ā4
Upregulation of the Obox family in Lin28 knocked down mESCs. Relative expression of the Obox family in Lin28 knocked down mESCs was confirmed by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The expression levels were calculated by computed tomography values, and the relative fold change was determined to compare the values of the control mESCs. The data are represented as the mean┬▒SD from 3 independent experiments. Obox, oocyte-specific homeobox; mESCs, embryonic stem cells; siCon, control siRNA transfected; siLin28, Lin28 siRNA transfected.