|
 |
- Search
| Clin Exp Reprod Med > Volume 42(2); 2015 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
The XIST gene is considered to be an attractive candidate gene for skewed X-chromosome inactivation and a possible cause of primary ovarian insufficiency (POI). The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the XIST gene promoter mutation is associated with idiopathic POI in a sample of the Korean population.
Methods
Subjects consisted of 102 idiopathic POI patients and 113 healthy controls with normal menstrual cycles. Patients with the following known causes of POI were excluded in advance: cytogenetic abnormalities, prior chemo- or radiotherapy, or prior bilateral oophorectomy. Genotyping was performed using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis.
Results
The mean age of onset of ovarian insufficiency was 28.7┬▒8.5 years and the mean values of serum luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones and estradiol in the POI group were 31.4┬▒18.2 mIU/mL, 74.5┬▒41.1 mIU/mL, and 30.5┬▒36.7 pg/mL, respectively. We found no cytosine to guanine (C43G) variation in the XIST gene in both POI patients and controls.
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), formerly known as premature ovarian failure or premature menopause, is characterized by amenorrhea for 4 months or more in association with increased serum gonadotropin concentration and hypoestrogenism before or at the age of 40 years [1,2]. This condition occurs in approximately 1 in every 100 women before the age of 40 years and 1 in every 1,000 women before the age of 30 years [3,4]. Idiopathic POI, the etiology of which remains unknown, may be related to underlying aberrations in parts of the X-chromosome related to maintaining ovarian function, which in turn might cause ovarian insufficiency.
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a process by which one of the two X-chromosomes is randomly inactivated to equalize X-linked gene dosage between XX females and XY males [5]. The X-inactivation process is controlled by a single X-linked cis-acting locus called the X-inactivation center (Xic) [6]. The X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) gene, whose product is a non-coding nuclear RNA, has been implicated strongly in the process of XCI [7]. The XIST gene, which maps to the Xic region on the X chromosome (Xq13.2), is exclusively expressed from inactive X chromosomes and its expression is tightly correlated with the presence of inactive X chromosomes [6,7,8]. Nonrandom, preferential X-inactivation has been found in female carriers of several X-linked syndromes [9,10,11]. Recently, there have been reports that a cytosine to guanine (C43G) mutation in the promoter region of the XIST gene is associated with skewed XCI [12,13,14,15,16] and, furthermore, that skewed XCI is associated with POI [17]. Plenge et al. [12] described nine females from two unrelated families who carried a promoter mutation in the XIST gene showed skewed XCI, and Sato et al. [17] reported that the incidence of skewed XCI was significantly higher in POI patients compared with controls (54.2% vs. 27.6% on Ōēź70% skewing; 37.5% vs. 13.8% on Ōēź80%; and 20.8% vs. 0.0% on Ōēź90%).
Considering these reports, it could be postulated that variation in the XIST gene leads to a preferential silencing of genes on the X chromosome related to the maintenance of ovarian function, and that this may serve as a susceptibility factor for POI. Therefore, the XIST gene is an attractive candidate gene for skewed XCI, which has been documented in the structural abnormalities of the X-chromosome, and could have a role in the pathogenesis of idiopathic POI. However, most studies of XIST mutation have focused on animals, and there is no large-scale association study in humans linking XIST mutation and POI. Even though we previously reported no significant difference in the incidence of skewed XCI between POI and control groups [18], it is still possible that underlying X-chromosome aberration is associated with idiopathic POI. Because the exact functional relationship between skewed XCI and POI is not yet elucidated, searching for genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, including skewed XCI, as risk factors for idiopathic POI is worthwhile.
In this study, we therefore investigated whether variation in the XIST gene is associated with idiopathic POI in a sample of the Korean population. To do this, we analyzed the frequency of the C43G mutation in the promoter region of XIST in patients with idiopathic POI and in controls.
A total of 102 idiopathic POI patients were enrolled, comprising 11 cases (10.8%) with primary amenorrhea and 91 cases (89.2%) with secondary amenorrhea. The applied diagnostic criteria for POI were as follows: Ōēź4 months of amenorrhea and two serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels of Ōēź40 mIU/ml obtained Ōēź1 month apart in women aged Ōēż40 years [1]. All patients underwent gynecological examination with pelvic ultrasound evaluation and complete POI workup including autoimmune disease and karyotype analysis as described previously [18]. Patients with known causes of POI (i.e., cytogenetic abnormalities, previous chemo- or radiotherapy or bilateral oophorectomy) were excluded from this study. A total of 113 women who had normal menstrual cycles (21-35 days) and normal ovarian features according to ultrasonography served as controls. The review board for human research of Seoul National University Hospital approved this study and written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Genomic DNA was isolated and extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes using the Wizard DNA purification kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Analysis of the XIST C43G mutation was carried out using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restriction fragment length polymorphism assay. The PCR reaction mixture had a total volume of 25 ┬ĄL and contained 0.025 ┬Ąg genomic DNA, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.3, 50 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 200 ┬ĄM dNTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates), 1 U Taq polymerase (Takara, Shiga, Japan) and 0.4 ┬ĄM of each upstream and downstream primer. The oligonucleotide primers used in PCR were as follows: forward 5'-GAGAGATCTTCAGTCAGGAAG-3' and reverse 5'-AGACCAGGAGTCACAACTTC-3'. The PCR cycling conditions were as follows: an initial denaturation step at 94Ōäā for 5 minutes, amplification for 35 cycles of PCR at 94Ōäā for 30 seconds, 55Ōäā for 30 seconds, and 72Ōäā for 30 seconds, followed by a final extension time of 5 minutes at 72Ōäā. PCR products were digested with 2 U of restriction enzyme HhaI (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) at 37Ōäā for 3 hours, separated by 3% agarose gel electrophoresis, and identified by using ethidium bromide staining.
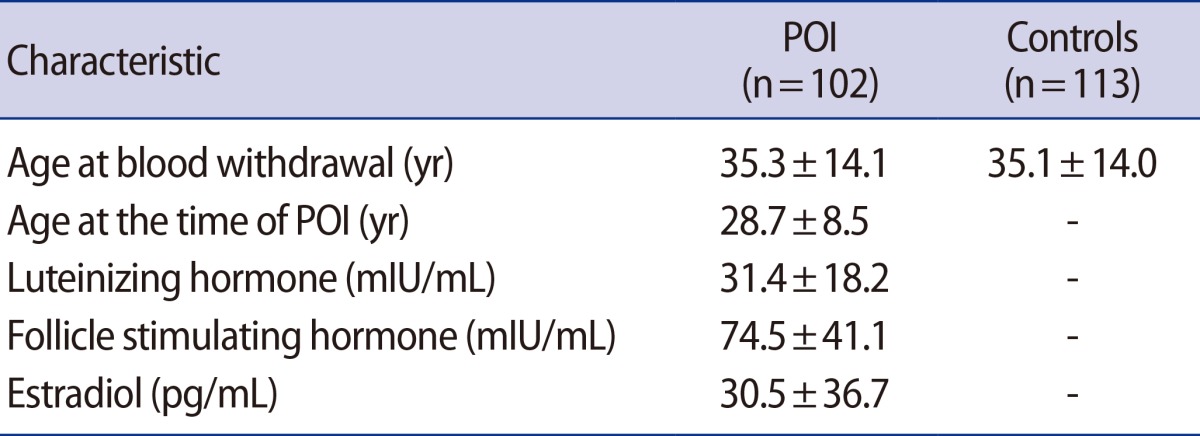
We investigated promoter mutations in the XIST gene in 102 patients with idiopathic POI and 113 normo-ovulatory women. The mean age of onset of POI was 28.7┬▒8.5 (standard deviation) years and the mean age at the time of blood withdrawal was 35.3┬▒14.1 years. The mean age of the control group was 35.1┬▒14.0 years. The mean values of luteinizing hormone (LH), FSH, and estradiol in the POI group were 31.4┬▒18.2 mIU/mL, 74.5┬▒41.1 mIU/mL, and 30.5┬▒36.7 pg/mL, respectively (Table 1).
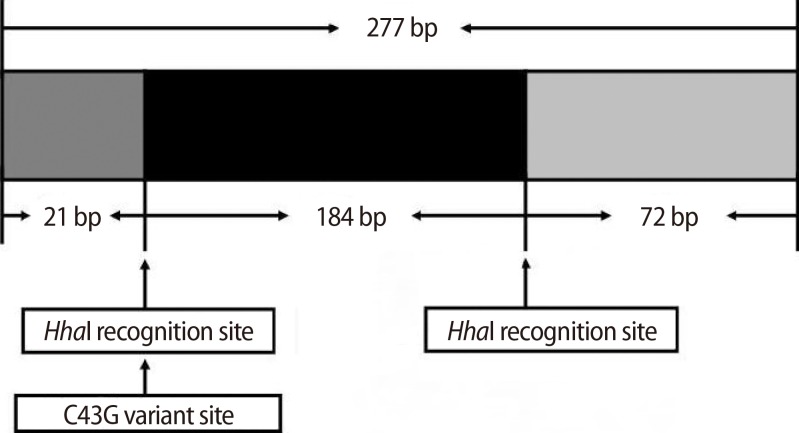
The homozygous wild-type product yields a common cut, i.e., two fragments of 205 and 72 bp, when digested with HhaI. In the presence of a C43G variant, the product is cut into three fragments of 184, 72, and 21 bp for homozygous mutant type (Figure 1). The genotype for the C43G variation was successfully determined in all subjects. Our analysis showed no mutation in either the POI or the control group (Table 2). There were only two bands (205 and 72 bp in size) in all subjects. This result was confirmed by sequencing analysis in both the POI and control groups.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the association of genetic variation in the promoter region of the XIST gene with idiopathic POI susceptibility in Korean women. In contrast to our expectation, there was no C43G mutation in the XIST gene in any of the subjects. Based on our results, C43G variation in the promoter region of the XIST gene may be rare in the Korean population. More importantly, our results suggest that the role of the XIST gene in the pathogenesis of POI is not yet clear. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to examine the association between the XIST gene variations and idiopathic POI.
X-chromosome aberrations such as Turner's syndrome are well known causes of POI. Considering the underlying genetic role of the sex chromosome in the maintenance of ovarian function, the preferential X-inactivation process by which most of the genes on the associated X chromosome are silenced could result in ovarian insufficiency before or at the age of 40. The most well-known genetic region involved in the process of X-inactivation is Xic. The XIST gene, which maps to the Xic region, is expressed exclusively from inactive X chromosomes and has been implicated in inactivation signaling [6]. A report that nine females from two unrelated families who carried a promoter mutation in the XIST gene showed skewed XCI, suggested that regulation of XIST gene expression is associated with XCI [12]. However, it has also been reported that this mutation is not present in 66 Brazilian females with skewed XCI [19]. In our cohort, there was no XIST mutation, and this finding is consistent with the latter Brazilian report.
The discrepancy in XIST promoter variation between studies could be explained as follows. First, ethnic differences in genetic studies require specific attention because they might influence the pattern of XIST promoter variation in POI patients. Studies from different populations are needed to replicate and confirm our results in idiopathic POI. Second, the previous report in which a promoter mutation in the XIST gene was associated with skewed XCI came from a family tree study. Both genetic and environmental factors are often related to the development of genetic variation, and these could affect menopausal age. Further study of XIST mutation in familial POI using large sample sizes will be helpful to elucidate these associations. Finally, it is also possible that C43G mutation in the promoter region of the XIST gene is neither necessary nor sufficient to promote preferential XCI in humans. Although the expression of the XIST gene is associated with X inactivation in mice [8], the functional significance of the C43G mutation in the human XIST promoter region is not yet clear. Our finding suggests that variation in genes related to the XCI process might not be a major determinant of the risk of idiopathic POI. There is some evidence that POI may partly depend on genetic factors [20,21]. However, it is unlikely that POI represents a single gene defect and it is more likely to be a polygenic or oligogenic trait. The cause of POI in terms of genetic aberration is unclear and much more research has to be done in this area.
Although our study found no association between XIST promoter variation and idiopathic POI, the results need to be interpreted with caution. The XIST gene encoding the Xic seems to play an important role in regulating XCI [8]. The roles of XIST in X-inactivation signaling and in the pathophysiology of POI remain to be investigated fully, especially in light of the inconsistent results of replication studies. Elucidation of factors involved in this genetic process could be helpful in understanding the underlying mechanisms of POI.
In summary, we found no C43G promoter variation in the XIST gene in patients with idiopathic POI in our sample of the Korean population. Although the present finding suggests that the role of the XIST gene in the pathogenesis of POI is not yet clear, there is increasing evidence that some underlying genetic aberration may cause X-chromosome abnormalities, which may be a risk factor for idiopathic POI. The potential relationship between variation in the XIST gene and POI remains to be investigated in diverse ethnic groups, and thus XIST gene expression may still have a role in pathophysiology of idiopathic POI.
Notes
References
2. Nelson LM. Clinical practice: primary ovarian insufficiency. N Engl J Med 2009;360:606-614.PMID: 19196677.



3. Coulam CB, Adamson SC, Annegers JF. Incidence of premature ovarian failure. Obstet Gynecol 1986;67:604-606.PMID: 3960433.


4. Goswami D, Conway GS. Premature ovarian failure. Hum Reprod Update 2005;11:391-410.PMID: 15919682.


5. Lyon MF. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature 1961;190:372-373.PMID: 13764598.


6. Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R, et al. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 1991;349:38-44.PMID: 1985261.


7. Hendrich BD, Plenge RM, Willard HF. Identification and characterization of the human XIST gene promoter: implications for models of X chromosome inactivation. Nucleic Acids Res 1997;25:2661-2671.PMID: 9185579.



8. Herzing LB, Romer JT, Horn JM, Ashworth A. Xist has properties of the X-chromosome inactivation centre. Nature 1997;386:272-275.PMID: 9069284.


9. Wengler G, Gorlin JB, Williamson JM, Rosen FS, Bing DH. Nonrandom inactivation of the X chromosome in early lineage hematopoietic cells in carriers of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Blood 1995;85:2471-2477.PMID: 7537115.


10. Orstavik KH, Orstavik RE, Eiklid K, Tranebjaerg L. Inheritance of skewed X chromosome inactivation in a large family with an X-linked recessive deafness syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1996;64:31-34.PMID: 8826445.


11. Devriendt K, Matthijs G, Legius E, Schollen E, Blockmans D, van Geet C, et al. Skewed X-chromosome inactivation in female carriers of dyskeratosis congenita. Am J Hum Genet 1997;60:581-587.PMID: 9042917.


12. Plenge RM, Hendrich BD, Schwartz C, Arena JF, Naumova A, Sapienza C, et al. A promoter mutation in the XIST gene in two unrelated families with skewed X-chromosome inactivation. Nat Genet 1997;17:353-356.PMID: 9354806.


13. Marahrens Y, Loring J, Jaenisch R. Role of the Xist gene in X chromosome choosing. Cell 1998;92:657-664.PMID: 9506520.


14. Newall AE, Duthie S, Formstone E, Nesterova T, Alexiou M, Johnston C, et al. Primary non-random X inactivation associated with disruption of Xist promoter regulation. Hum Mol Genet 2001;10:581-589.PMID: 11230177.


15. Nesterova TB, Johnston CM, Appanah R, Newall AE, Godwin J, Alexiou M, et al. Skewing X chromosome choice by modulating sense transcription across the Xist locus. Genes Dev 2003;17:2177-2190.PMID: 12952890.



16. Pugacheva EM, Tiwari VK, Abdullaev Z, Vostrov AA, Flanagan PT, Quitschke WW, et al. Familial cases of point mutations in the XIST promoter reveal a correlation between CTCF binding and pre-emptive choices of X chromosome inactivation. Hum Mol Genet 2005;14:953-965.PMID: 15731119.


17. Sato K, Uehara S, Hashiyada M, Nabeshima H, Sugawara J, Terada Y, et al. Genetic significance of skewed X-chromosome inactivation in premature ovarian failure. Am J Med Genet A 2004;130:240-244.PMID: 15378546.

18. Yoon SH, Choi YM, Hong MA, Kang BM, Kim JJ, Min EG, et al. X chromosome inactivation patterns in patients with idiopathic premature ovarian failure. Hum Reprod 2008;23:688-692.PMID: 18182395.


19. Pereira LV, Zatz M. Screening of the C43G mutation in the promoter region of the XIST gene in females with highly skewed X-chromosome inactivation. Am J Med Genet 1999;87:86-87.PMID: 10528256.


20. Therman E, Laxova R, Susman B. The critical region on the human Xq. Hum Genet 1990;85:455-461.PMID: 2227929.


21. Davis CJ, Davison RM, Payne NN, Rodeck CH, Conway GS. Female sex preponderance for idiopathic familial premature ovarian failure suggests an X chromosome defect: opinion. Hum Reprod 2000;15:2418-2422.PMID: 11056145.