|
 |
- Search
| Clin Exp Reprod Med > Volume 41(3); 2014 > Article |
Abstract
The placenta is a temporary fetomaternal organ capable of supporting fetal growth and development during pregnancy. In particular, abnormal development and dysfunction of the placenta due to cha nges in the proliferation, differentiation, cell death, and invasion of trophoblasts induce several gynecological diseases as well as abnormal fetal development. Autophagy is a catalytic process that maintains cellular structures by recycling building blocks derived from damaged microorganelles or proteins resulting from digestion in lysosomes. Additionally, autophagy is necessary to maintain homeostasis during cellular growth, development, and differentiation, and to protect cells from nutritional deficiencies or factors related to metabolism inhibition. Induced autophagy by various environmental factors has a dual role: it facilitates cellular survival in normal conditions, but the cascade of cellular death is accelerated by over-activated autophagy. Therefore, cellular death by autophagy has been known as programmed cell death type II. Autophagy causes or inhibits cellular death via the other mechanism, apoptosis, which is programmed cell death type I. Recently, it has been reported that autophagy increases in placenta-related obstetrical diseases such as preeclampsia and intrauterine growth retardation, although the mechanisms are still unclear. In particular, abnormal autophagic mechanisms prevent trophoblast invasion and inhibit trophoblast functions. Therefore, the objectives of this review are to examine the characteristics and functions of autophagy and to investigate the role of autophagy in the placenta and the trophoblast as a regulator of cell death.
During pregnancy, the placenta is a fetomaternal organ that connects the mother and baby through the umbilical cord and supports fetal development via the transport of gases, nutrients, waste, etc. The structures of the placenta include the umbilical cord, fetal membranes including the amnion and the chorion, many placental villi, and the basal plate connecting to the myometrium of the maternal uterus [1]. In particular, the trophoblast gives rise to placental tissues, which secrete several cytokines that enable pregnancy to be maintained. The placenta is derived from the trophectoderm in the outer layers of blastocysts in the early stages of pregnancy. In particular, the cytotrophoblast, which originates from the trophectoderm, rapidly differentiates into the syncytiotrophoblast when the cytotrophoblast makes contact with the endometrium of the maternal myometrium, resulting in infiltration into the extracellular matrix of the endometrium and implantation [2]. The placenta develops by dynamic cellular processes such as the proliferation, differentiation, and death of invasive trophoblasts and involves normal placentation as well as fetal development. However, abnormal placental development due to trophoblast dysfunction causes severe gynecological diseases and several fetal malformations [1,2]. In particular, proliferation and cell death in the trophoblast is an important factor in placental development [3]. Syncytiotrophoblasts are formed by the fusion of cytotrophoblasts during trophoblast differentiation and assume the function of trophoblasts by forming syncytial knots through syncytial fusion, resulting in aggregated nuclei. Syncytiotrophoblasts die by apoptosis during the placental aging process and are then discharged into the peripheral blood of the mother. The loss of syncytiotrophoblasts in the placenta is maintained by cytotrophoblasts in the inner part of the placental villi, and the syncytiotrophoblast rapidly recovers through the proliferation and differentiation of cytotrophoblasts.
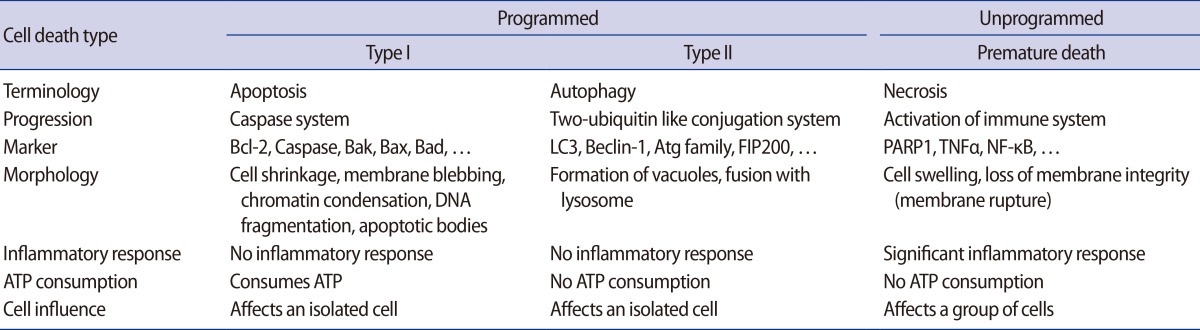
There are three types of cell death (Table 1). Necrosis, which is unprogrammed cell death, induces inflammation in cells by immunological activation and causes death in neighboring cells. In contrast, programmed cell death type I (apoptosis) and type II (autophagy) progress through special programs for cell death [4]. Depending on the cell type, there are correlations between apoptosis and autophagy, which are dependent and independent in distinct steps of their respective programs for cell death [5,6]. However, autophagy does not consume adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) in the processing of cell death, as apoptosis does. Furthermore, autophagic structures fused with lysozymes (e.g., autolysosomes) located in the cytoplasm are different from those observed during apoptosis (e.g., randomly fragmented nuclei). Several factors including intrinsic (e.g., nutrient starvation) and extrinsic (e.g., hypoxia or stress) factors trigger the unique characteristics of activated autophagy involved in cell death and cell survival [7]. For this reason, many studies have reported multiple roles of autophagy in biological and developmental processes in the cell. However, the mechanisms and pathways of autophagy in placental development and gynecological diseases are still unclear. Therefore, we will address the characteristics of autophagy and its regulation mechanisms and discuss the roles of autophagy in the placenta and in placental diseases.
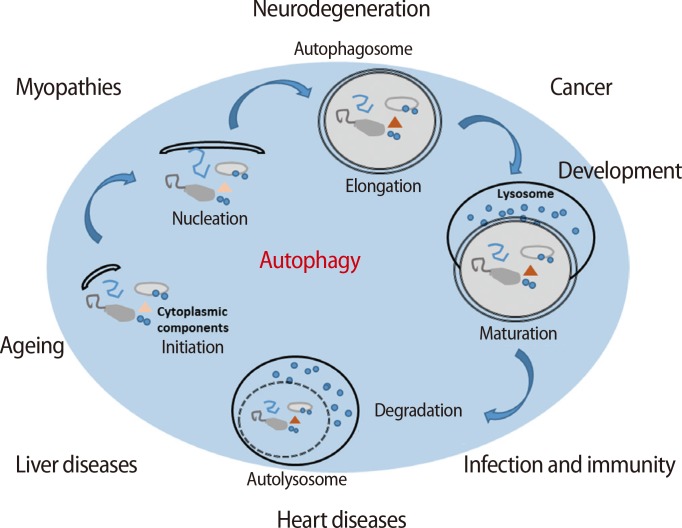
Autophagy, also known as autophagocytosis, is a catabolic mechanism that involves the digestion of damaged or dysfunctional cellular components through fusion with lysosomes [8,9]. Additionally, autophagy is necessary to maintain cellular homeostasis during proliferation, differentiation, and cell death as well as cellular survival during nutrient starvation or the blockage of metabolism in the cell [10]. There are five stages in the process of autophagy (Figure 1) [11,12]. During the initiation step, autophagy is triggered by the phosphorylation of the UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) kinase complex, which consists of ULK1, autophagy-related gene 3 (Atg3) and Atg17, and is activated by stress signals from the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 in damaged or dysfunctional cells [13]. The activated ULK1 complex activates the phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K) complex type 3, resulting in the formation of an autophagosome, which is a structure consisting of cellular membrane as nucleation process [14,15]. After nucleation, an autophagosome is generated by the expression of the Atg family [16]. In the maturation step, an autolysosome is formed by the fusion of an autophagosome and a lysosome. Finally, in the degradation step, the final cellular building blocks are completely digested in the autolysosome with several lysozymes secreted into the cytoplasm. Therefore, autophagy helps to maintain cellular survival in normal conditions; conversely, it also promotes cell death when cells are activated by the digestion of cellular components or the presence of microorganisms in abnormal conditions, such as stress, or nutrient starvation [17].
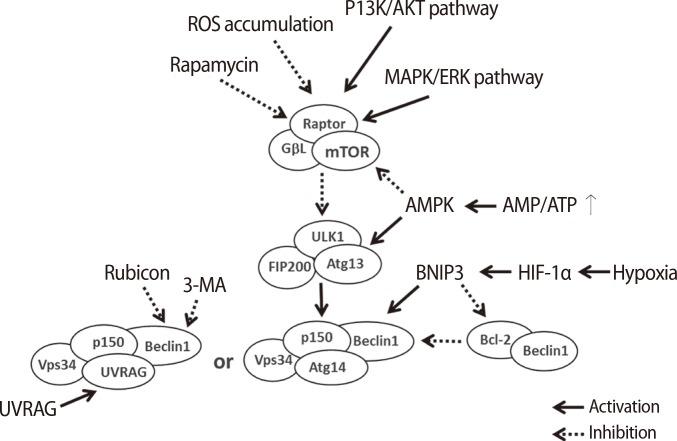
Generally, moderate levels of autophagy help to maintain the development and differentiation of cells and also maintain cellular survival through the resynthesis of cell building blocks, which are digested in intracellular organelles or proteins, even when cell metabolism is suppressed [8,9]. There are several factors in each step of autophagy because the mechanism controlling autophagy is complex (Figure 2) [11,18,19]. Initially, the mTOR complex induces the phosphorylation of ULK1, which is a type of Ser/Thr protein kinase, and Atg13 when autophagy is not activated. The ULK1 complex, which consists of ULK1, Atg13, and family interacting protein of 200 kD (FIP200), is inactivated by phosphorylation via the mTOR complex [20,21,22]. However, the ULK1 complex prevents itself from being phosphorylated, and ULK1 triggers the dephosphorylation of FIP200, Atg13, and itself when the mTOR complex is inactivated by environmental signaling (e.g., nutrient starvation or reactive oxygen species [ROS] accumulation). The FIP200-Atg13-ULK1 complex acts as a node for integrating incoming autophagy signals during autophagosome formation [17]. In normal conditions, Beclin-1 binds to one of the Bcl-2 family proteins, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, or Mcl-1; however, the complex breaks down by specific signaling [23,24]. Beclin-1 is bound to PI3K by the ULK1 complex, and the complex gradually binds to p150, AMBRA1, UVRAG, and ATG14/BARKOR [25]. The PI3K complex type 3 is formed by these complexes, and the resulting complex is involved in the nucleation step of autophagy. Therefore, the complex formation controls the activation level of autophagy through inhibition to combine the autophagosome and the lysosome in the complex by binding Rubicon [19]. However, the nucleation step occurs in the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum or the mitochondria by the activation of the PI3K complex type 3. The PI3K complex activated by the ULK1 complex forms PI3P on the membrane, resulting in an autophagosome formed on a chipped-off fragment of the membrane. The membrane used in this step is referred to as an isolation membrane, and this process is referred to as nucleation. Atg family proteins are involved in the formation of the autophagosome at this point [18]. Initially, the autophagy-related protein 12 (Atg12) conjugation system is activated by the binding of the glycine residue on the C-terminal of Atg12 and Atg7, which is a ubiquitin E1-like protein. Furthermore, activated Atg12 promotes isopeptide formation through the binding of Atg10, which is an E2-like protein, to the glycine residue of activated Atg12 and the lysine of Atg5. Then, Atg16 forms the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex by binding to the Atg12-Atg5 complex. In the Atg8 (light chain 3, LC3) conjugation system, Atg4 is capable of cysteine proteinase digestion to remove the arginine residue of the C-terminus of Atg8, which is bound to Atg3 by activated Atg7, and conjugated Atg3 mediates the binding of Atg8 and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). Formation of the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L complex from these steps involves expanding the autophagosome, resulting in the complex molecules being scattered into the cytoplasm. Additionally, the Atg8-PE complex is involved in the expansion of the autophagosome and is a useful component for autophagosome formation because it exists on the membrane of the autophagosome before lysosome binding. Elongation during autophagy is the process of forming the autophagosome via a ubiquitin-like conjugation system after the nucleation step. The maturation step of autophagy is the process of binding the lysosome to the autophagosome. The binding of the autophagosome and the lysosome induces the digestion of damaged cellular organelles by lysosomal enzymes, resulting in the release of the final digested products into the cytoplasm. These are the degradation steps of autophagy. The digested molecules, including amino acids and fatty acids, are recycled as cell building blocks or an energy source for cellular survival or the resynthesis of cellular organelles [16].
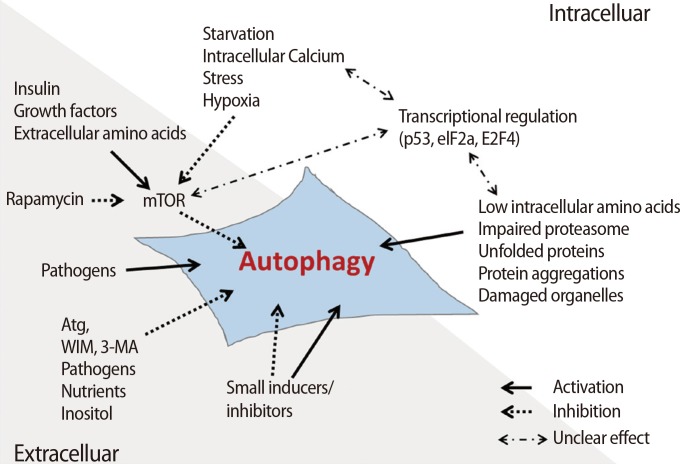
Autophagy-related factors are divided into intrinsic factors in cells and extrinsic factors affecting the surrounding microenvironment of cells (Figure 3). The intrinsic factors within cells are regulated by nutrient starvation, the concentration of Ca2+, transcriptional genes, the concentration of amino acids, damage to the proteosome, and the accumulation of compounds secreted from damaged cells or microorganelles to maintain cell survival [26,27]. Cells must produce sources of energy to support metabolism when undernourished. Therefore, cells digest several compounds through autophagy to supplement deficient nutrients or energy. Increased Ca2+ concentration in the cytoplasm activates calmodulin (CaM), which triggers CaMKK╬▓ activation and inhibits the phosphorylation of the mTOR complex [28]. Additionally, CaM activates DAPK, thus accelerating the phosphorylation of Beclin-1. Phosphorylated Beclin-1 separates into Beclin-1 and Bcl-2, resulting in Beclin-1 activation [29,30]. Therefore, the concentration of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm of cells triggers activation of the autophagic mechanism.
It is well known that hypoxia is involved in cell survival as well as cell death through the activation of autophagy [31,32]. Activated hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) under hypoxic conditions activates the BH3-only proteins BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) and BNIP3L through Beclin-1 combined with Bcl-2/Bcl-xL or the BH3 domain [33]. During this process, the activated BNLP3/BNIP3L complex binds to Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL and induces the separation of Beclin-1 to form the complex.
Transcriptional factors are also involved in the activation of autophagy. In particular, p53, which is a tumor suppressor gene, inhibits the G1-to-M phase transition through phosphorylation of p53 when cells are exposed to nutrient starvation, such as a lack of glucose. These processes help to maintain cellular survival. In cytotoxic stress conditions, p53 is activated as a transcriptional factor and promotes the activation of transcription factors related to autophagy such as Sestrin 1/2, TSC2, and 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) ╬▓1/╬▓2 [34]. Generally, the expression of these genes triggers the activation of autophagy through the inhibition of mTOR; however, inactive p53 in the cytoplasm inhibits autophagy through the inhibition of the ARF transcription factor in normal conditions [35]. Additionally, autophagy is regulated by other transcriptional factors, including eIF2╬▒ and FOXO3, which are capable of controlling the expression of the Atg family.
Autophagy is also activated by ROS, which accumulate in nutrient-deficient conditions [36], and mitochondrial DNA damage or deletions. AMPK is activated by dysfunctional mitochondrial proteins derived from inadequate ATP production by damaged mitochondrial DNA. Activated AMPK activates autophagy via the inhibition of mTOR [37]. 3-Methyladenine (3-MA), as an extrinsic factor, is a representative inhibitor of autophagy through block conversion of LC3 by the suppression of PI3K. Rapamycin can directly inhibit mTOR and is used as a representative extrinsic factor that activates autophagy [38]. Also, insulin inhibits autophagy through the activation of mTOR by regulating the concentration of glucose in the cell. Moreover, bacteria, inositol, and nutrients entering the cell are involved in the activation of autophagy [27].
During cellular events, autophagy is required to maintain cell survival as well as to induce cell death according to cell type or autophagy-related factor. For example, autophagy in cancer is involved in cellular survival through the activation of autophagy in abnormal conditions (e.g., nutrient deficiency, hypoxia); conversely, autophagy suppresses the growth of cancer cells or induces the death of cancer cells exposed to chemical injury or radiation [12]. Additionally, autophagy helps to inhibit the proliferation and growth of tumors by suppressing angiogenesis. Autophagy induces the death of cancer cells when ARHI, a tumor suppressor gene, inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway [39]. At this point, relevant cell growth factors and pro-angiogenesis factors activate autophagy, resulting in an involvement of autophagy in the proliferation, survival, or death of cancer cells that is dependent on the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Although autophagy can be a tool for the survival of most cells in poor conditions, autophagy can also induce the death of cells via digestion processing, regardless of the normal and damaged components in cells in over-activation of autophagy by abnormal conditions, such as apoptosis or cellular injuries by infectious pathogens [40]. For the reason, many scientists have been focused on the over-activation of autophagy as a therapy against cancer cells and have demonstrated that autophagy can inhibit the development of cancer by inhibiting the accumulation of injured mitochondrial DNA. Thus, it is important to maintain the homeostasis of autophagy for cell survival.
Generally, autophagy-related proteins activated by stress signals from cells suppress apoptosis, whereas activated apoptosis suppresses autophagy [41]. Additionally, the binding of Bcl-2 and Beclin-1 inhibits autophagy, whereas the inhibition of Bax suppress apoptosis [42]. Cells progress to apoptosis, which is type I programmed cell death, when their DNA is damaged or when externally stimulated. However, autophagy activated by the inhibition of apoptosis due to the lack of caspases, Bax, and Bak is type II programmed cell death [43]. The interaction between apoptosis and autophagy is regulated by autophagy-related factors such as Bcl-2, Atg5, and p53. However, their interaction and the detailed mechanism through which this takes place should be further studied in the future.
Although many studies have reported mechanisms for survival and death via autophagy, there are still multiple unclear functions of autophagy in cells depending on cellular conditions. Basically, the balance of autophagy in cells is important because excessively high or low rates of autophagy cause cell death. For example, activated autophagy in hepatocytes in a nutrient-deficient mouse model triggers gluconeogenesis by binding fatty acids and amino acids digested from other molecules or proteins in cells, which decreases insulin expression [44]. Thus, in this case, autophagy has the role of promoting cell survival by controlling the glucose level of blood. In contrast, autophagy triggers cell death in human hepatocellular carcinomas after being activated by the inactivation of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) [45]. Additionally, Komatsu et al reported that in the neuronal cells of an Atg7-deficient mouse model, a lack of autophagy induces neuronal diseases, which means that autophagy plays a role in neuronal survival [46]. Treating the rat neuronal PC12 cancer cell line with propofol enhanced the survival rate of cells via the inhibition of autophagy, and the results suggest that autophagy causes the death and survival of cells [47]. Additionally, autophagy-related neuronal diseases help cells to survive by maintaining homeostasis and preventing the buildup of toxic levels of intracellular proteins in cells [48]. However, a toxic form of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) can accumulate in the autophagosome because the intracellular accumulation of substances does not decompose gradually when a high level of autophagy induces the autophagosome to combine with the lysosome. It was reported that activated autophagy eventually causes cellular injury in these conditions. Also, autophagy in heart disease ensures the survival of myocardial cells through AMPK activation in myocardial infarction with glucose deficiency, whereas activated autophagy induces injury of cells when the expression of Beclin-1 is increased despite the inactivation of AMPK by perfusion [49,50]. Thus, abnormally activated autophagy causes the death of cells targeted in several diseases.
The blastocyst is formed after fertilization and attaches to the endometrium of the maternal uterus. The trophectoderm in the outer layer of the blastocyst differentiates into the trophoblast, and in turn, the trophoblast facilitates implantation through the secretion of enzymes, which cause the uterine lining to partially disassemble [2]. The blastocyst penetrates into the endometrium within approximately 7 to 12 days after fertilization. Then, the blastocyst in the inner layer differentiates into the cytotrophoblast, which is a mononuclear cell, whereas the blastocyst in the outer layer differentiates into the syncytiotrophoblast, which includes multinuclear cells, via cell to cell fusion. Finally, the layers of the trophoblast gradually grow, and lacunae begin to appear in the syncytiotrophoblast [7]. The trophoblast not only supplies nutrients from maternal blood but also protects the embryo and the fetus from maternal immunological attack. The lacunae eventually give rise to uteroplacental circulation and expand throughout the syncytiotrophoblast, which surrounds the blastocyst.
After fertilization, the embryo is nourished solely through diffusion for a week until the neovascularization and vascular remodeling process is established. During this time, the embryo is rapidly growing and requires increased nutritional supply. Maternal-fetal material exchange can be increased by the completed formation of the substantial area in which they are in contact during the development of the utero-placental circulation system, even though their blood flows are not directly connected. Approximately 12 days later, the cytotrophoblast starts to penetrate the endometrium, and the lacunae keep growing in the syncytiotrophoblast, which allows maternal arterial capillaries to fuse with the lacunae to form the intervillous space. Thirteen days after fertilization, the blastocyst completely enters the endometrium, and trophoblasts penetrate the syncytiotrophoblast, forming the primary chorionic villi. The outer layer of the placenta protrudes from the villi and is referred to as the chorionic plate. Secondary villi arise when the extraembryonic mesoderm starts to form from primary villi 16 days after fertilization. The extraembryonic mesoderm expands through the lacunae, which are filled with maternal blood. Almost 3 weeks later, the villous mesoderm differentiates into connective tissue and capillary vessels and connects embryonic blood vessels. This circulation system functions to circulate embryonic blood through villous capillary vessels. These structures are called tertiary villi. As the villi grow, the villi of the decidua capsularis degenerate to form the chorion laeve. The villi adjacent to the decidual plate rapidly grow to form the chorion frondosum. Then, the decidual plate and the chorion frondosum form the placenta. Four weeks later, as maternal blood flows into the placenta through spiral arteries and out through uterine veins, the basic structures of the placenta have been formed. Subsequently, all maternal-fetal material exchange occurs through the villous membrane surrounding the capillary vessels, the connective tissue surrounding the villous membrane, the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast, which form the placental barrier. The closest chorionic villus to maternal blood keeps growing and expanding in the chorionic tissue. By expanding the amniotic sac surrounding the embryo, the chorionic villi far from maternal blood are slowly pushed out and degenerate to form the chorionic layer. Twenty weeks after fertilization, the amnion, the chorion and the decidual layers appear to be complete structures. After 4 months, the placental structure is complete, and no further morphological changes occur. With this structure, the placenta helps the mother supply essential nutrients to the fetus [1].
Through the chorionic villi encircled by uterine spiral arteries, maternal blood flows into the entire placenta. The fetus absorbs maternal blood in through the placenta by two umbilical arteries spanning the placental surface. These arteries continue to spread into the placenta until the blood reaches the capillary vessels of chorionic villi, and maternal-fetal gas exchange takes place through these villi. Therefore, the chorionic villus can be regarded as the main structure performing the fundamental roles of the placenta. Additionally, the fetus releases waste materials into maternal blood through only one umbilical vein. The placenta also plays an important role in protecting the fetus against maternal immunological attacks, and the placental barrier helps to block harmful materials from flowing into the fetus from maternal blood. Moreover, by maintaining proper concentrations of hormones such as progesterone, estriol, and steroids, the placenta helps to maintain pregnancy and aids the activity of uterine muscles during pregnancy.
Autophagy in the normally developed placenta plays multiple very important roles in embryo development. It has been reported that embryonic or fetal death increases by inactivating autophagy-related genes in mouse models, and this result suggests that autophagy plays important roles in the survival of neonates during nutritional deficiency at the early stage of birth [51]. By administering rapamycin, which induces autophagy and represses the mTOR complex, autophagic activation has been shown to function as a repressing factor in the growth of cervical fascia. It was reported that the growth and remodeling of cervical fascia progresses by regulating autophagy through the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway during pregnancy [52]. Additionally, it has been reported that the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway regulates the differentiation of trophoblasts in a mouse model [53], but it has not yet been reported that autophagy affects the differentiation of trophoblasts in pregnant women by activating LC3-II and Beclin-1, direct markers of autophagy that were analyzed and compared between normally developed full-term placentas and placentas in women in their first trimester. The markers were observed in prevalently activated patterns in villous cytotrophoblasts in the placenta during the first trimester and were activated in the cytoplasm of trophoblasts in full-term placentas [54]. Through these characteristic changes of autophagic markers, the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast displayed distinctive activation in accordance with gestational age. Therefore, autophagy is essential for placental development and for maintaining pregnancy. It has also been reported that autophagy is induced in placentas with preeclampsia [55,56] and that LC3 activation is lower and placental apoptosis is higher in the placenta of women with gynecological disease than in normally developed pregnancies [57,58]. Therefore, which cells of the placenta undergo autophagy and how autophagy contributes to cell survival are still unclear. Additional studies are required regarding whether apoptosis and autophagic mechanisms inducing cell death function differently in cell survival during unfavorable conditions.
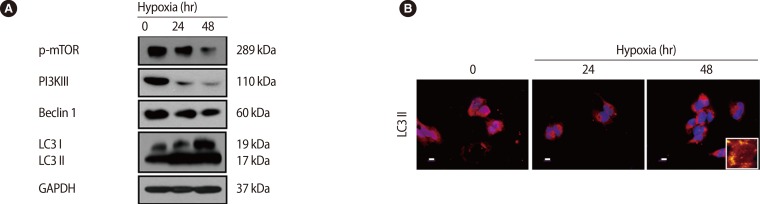
Trophoblasts are one of the main types of cells composing the placenta, and they help to maintain pregnancy by releasing pregnancy related cytokines. Additionally, trophoblasts are directly involved in implantation through their infiltration ability. The trophoblast, situated between the feto-placental unit and maternal blood, functions as a physical an d immunological barrier against pathogens in order to maintain fetal growth. Oxygen and glucose concentrations change with gestational age, and cytotrophoblastic autophagy changes in response in the trophoblast [59]. Recently, it has been reported that trophoblast-derived exosomes and chromosome 19 miRNA (C19MC) increase antiviral defense in the maternal-fetal interface by inducing autophagic activation [60]. Importantly, it was reported that trophoblastic autophagy is increased by hypoxia more than any other inducing factor. Normal placentation is accomplished by increasing autophagy, which is induced by physiological hypoxic conditions (17.9 mm Hg) in the early stage of pregnancy. However, autophagy-related protein 7 (Atg7), which is silenced by hypoxia, decreases LC3-II and apoptosis in human primary trophoblasts. Therefore, hypoxia has a dual role in apoptosis and autophagy in trophoblasts [61]. In our previous report, we showed that the overexpression of HIF-1╬▒ by hypoxia induces LC3-II activation and represses phosphorylated mTOR, and activated autophagy induce increased matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 expression, which increase trophoblast infiltration [62] (Figure 4). This increased trophoblast infiltration involves autophagy, which maintains homeostasis by consuming cellular energy induced by HIF-1╬▒ [63]. When induced by external factors such as hypoxia, autophagy directly affects trophoblast infiltration during normal placental development.
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) results in a low-weight fetus due to abnormal development. A fetus needs to develop sufficiently according to its genetic potency, but a fetus with IUGR is unable to grow or develop sufficiently without complete placentation. Although the cause of this condition is still unclear, it has been suggested that IUGR occurs when the spiral arteries are not completely developed due to abnormal penetration of the endometrium by the cytotrophoblast. In recent studies that compare normal pregnancy with IUGR, expression levels of LC3 and Beclin-1 and the formation of the autophagosome were observed, and it was found that abnormal placentation causing IUGR is related to the imbalance of cell homeostasis, which increases autophagy in the cytotrophoblast [64]. Other studies suggest that based on the expression of LC3, Beclin-1, and the Atg family, autophagy is found to be increased more in placentas with fetal growth restriction (FGR) than in normal placentas, and therefore, the main cause of FGR seems to be autophagy, which damages the development and function of the placenta [65]. Autophagic and apoptotic mechanisms sometimes appear to interact with each other [66]. Comparing the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast in normal pregnancy with IUGR, apoptosis is more frequent in IUGR [67]. Based on the result that autophagy is elevated in placentas with IUGR compared with normal placentas, autophagy might be an important factor in gynecological diseases.
Preeclampsia is a disorder involving hypertension with proteinuria during gestation. Preeclampsia leads to proteinuria of 300 mg/day or more throughout gestation and hypertension of 140/90 mm Hg or more after 20 weeks of gestation. Hypertension in the first 20 weeks of gestation is called chronic hypertension, and hypertension after 20 weeks without proteinuria is referred to as gestational hypertension. Eclampsia includes convulsions and paroxysms that happen at 6-7 months gestation. Thus, it is a disorder of the fetus capable of inducing damages at the end of pregnancy. The main causes of preeclampsia are not yet known, but many studies are still being conducted to clarify the relevant mechanisms. However, it was recently suggested that the syncytiotrophoblast penetrates abnormally into the endometrium after implantation and results in a reduced blood supply to the fetus from the mother, leading to hypertension and preeclampsia. One of the majors causing of this condition is extreme ROS accumulation resulting in deficient antioxidant protection [68]. Because ROS accumulation functions as an activator of autophagy, the research for demonstrating the relationship between autophagy and preeclampsia is ongoing. The expressions of the autophagic markers (e.g., LC3, Beclin-1, autophagosome formation) are shown to have different patterns during normal pregnancy and pregnancy with preeclampsia because various environmental factors including hypoxia control their expression. It has been reported that autophagic markers in the JEG-3 cell line (the human placental choriocarcinoma cell line) were increased when they were exposed to hypoxia [56]. Because the suggested cause of preeclampsia is oxygen stress, cells were exposed to hypoxic conditions in vitro to obtain a similar model of the placenta with preeclampsia [69]. According to research on trophoblasts in placenta with preeclampsia, the expression of Beclin-1 and LC3 and the autophagosome formation level were shown to be higher than in normal placentas [70]. Additionally, autophagy and apoptosis were shown to be higher in placentas with preeclampsia than in normal placentas [71]. It was reported that poor placentation is induced by decreased infiltration of trophoblasts due to abnormal processing for autophagy, which is activated by soluble endoglin (sENG), a substance detected in blood plasma during pregnancy with preeclampsia [72,73]. Also, it was reported that the inactivation of autophagy represses trophoblast infiltration and vascular remodeling due to excessive hypoxia, causing poor placentation, as observed in preeclampsia [74]. Based on these results, autophagy is regulated during placentation and appears to be a possible factor in preeclampsia, but further studies are required.
Autophagy plays an important role in cell survival and is induced by various factors. Additionally, autophagy leads to cell death according to cell conditions and certain mechanisms. This process functions in cell growth and development by using the building blocks that result from cell death. Autophagy is also induced in trophoblasts throughout placentation. Autophagy in the placenta aids in the development and remodeling of the endometrium, removing damaged cell organelles, maintaining cell homeostasis and the differentiation and infiltration activity of trophoblasts. Although the mechanism is still unclear, it seems to help maintain proper maternal-fetal material exchange during normal placental development. Additionally, abnormal regulation of autophagy is involved in various diseases. In gynecological diseases related to the placenta, abnormal placental development can arise from abnormally regulated autophagy due to external factors, such as hypoxia, that affect fetal development. In previous studies, the expression of autophagy markers, such as LC3-II, Beclin-1, and the Atg family, were detected in several gynecological diseases such as preeclampsia and IUGR. These studies suggest that autophagy is a possible factor in normal placentation as well as obstetrical diseases, but the precise mechanism requires further research.
Notes
References
1. Benischke K, Kaufmann P. Pathology of the human placenta. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2000.
2. Moore KL, Persaud TV. The developing human-clinically orientated embryology. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008.
4. Berry DL, Baehrecke EH. Autophagy functions in programmed cell death. Autophagy 2008;4:359-360.PMID: 18212526.



5. Rikiishi H. Novel Insights into the Interplay between Apoptosis and Autophagy. Int J Cell Biol 2012;2012:317645PMID: 22496691.



6. Levine B, Sinha S, Kroemer G. Bcl-2 family members: dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy. Autophagy 2008;4:600-606.PMID: 18497563.


7. Cross JC. How to make a placenta: mechanisms of trophoblast cell differentiation in mice: a review. Placenta 2005;26(Suppl A): S3-S9.PMID: 15837063.


8. Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 2004;6:463-477.PMID: 15068787.


10. Mizushima N, Levine B. Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 2010;12:823-830.PMID: 20811354.



11. Ichimura Y, Komatsu M. Pathophysiological role of autophagy: lesson from autophagy-deficient mouse models. Exp Anim 2011;60:329-345.PMID: 21791873.


12. Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 2008;451:1069-1075.PMID: 18305538.



13. Jung CH, Jun CB, Ro SH, Kim YM, Otto NM, Cao J, et al. ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol Biol Cell 2009;20:1992-2003.PMID: 19225151.



14. Di Bartolomeo S, Corazzari M, Nazio F, Oliverio S, Lisi G, Antonioli M, et al. The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian autophagy. J Cell Biol 2010;191:155-168.PMID: 20921139.



15. Hailey DW, Rambold AS, Satpute-Krishnan P, Mitra K, Sougrat R, Kim PK, et al. Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation. Cell 2010;141:656-667.PMID: 20478256.



16. Yang Z, Klionsky DJ. An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2009;335:1-32.PMID: 19802558.



17. Codogno P, Meijer AJ. Autophagy and signaling: their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death Differ 2005;12(Suppl 2): 1509-1518.PMID: 16247498.


18. Wang CW, Klionsky DJ. The molecular mechanism of autophagy. Mol Med 2003;9:65-76.PMID: 12865942.



19. Zhong Y, Wang QJ, Li X, Yan Y, Backer JM, Chait BT, et al. Distinct regulation of autophagic activity by Atg14L and Rubicon associated with Beclin 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase complex. Nat Cell Biol 2009;11:468-476.PMID: 19270693.



20. Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol 2011;13:132-141.PMID: 21258367.



21. Hosokawa N, Hara T, Kaizuka T, Kishi C, Takamura A, Miura Y, et al. Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 2009;20:1981-1991.PMID: 19211835.



22. Ganley IG, Lam du H, Wang J, Ding X, Chen S, Jiang X. ULK1.ATG13.FIP200 complex mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for autophagy. J Biol Chem 2009;284:12297-12305.PMID: 19258318.



23. Marquez RT, Xu L. Bcl-2:Beclin 1 complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle switch. Am J Cancer Res 2012;2:214-221.PMID: 22485198.


24. Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N, et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005;122:927-939.PMID: 16179260.


25. Itakura E, Kishi C, Inoue K, Mizushima N. Beclin 1 forms two distinct phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes with mammalian Atg14 and UVRAG. Mol Biol Cell 2008;19:5360-5372.PMID: 18843052.



26. Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G. Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007;8:741-752.PMID: 17717517.


27. Jaeger PA, Wyss-Coray T. All-you-can-eat: autophagy in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Mol Neurodegener 2009;4:16PMID: 19348680.



28. Grotemeier A, Alers S, Pfisterer SG, Paasch F, Daubrawa M, Dieterle A, et al. AMPK-independent induction of autophagy by cytosolic Ca2+ increase. Cell Signal 2010;22:914-925.PMID: 20114074.


29. Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Mizrachy L, Idelchuk Y, Koren I, Eisenstein M, et al. DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of autophagy. EMBO Rep 2009;10:285-292.PMID: 19180116.



30. Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Eisenstein M, Kimchi A. Phosphorylation of Beclin 1 by DAP-kinase promotes autophagy by weakening its interactions with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. Autophagy 2009;5:720-722.PMID: 19395874.


31. Song ZC, Zhou W, Shu R, Ni J. Hypoxia induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death in human periodontal ligament cells through HIF-1alpha pathway. Cell Prolif 2012;45:239-248.PMID: 22429763.



32. Hu YL, DeLay M, Jahangiri A, Molinaro AM, Rose SD, Carbonell WS, et al. Hypoxia-induced autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and adaptation to antiangiogenic treatment in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 2012;72:1773-1783.PMID: 22447568.



33. Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P, Chiche J, Roux D, Pouyssegur J, et al. Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol 2009;29:2570-2581.PMID: 19273585.



34. Budanov AV, Karin M. p53 target genes sestrin1 and sestrin2 connect genotoxic stress and mTOR signaling. Cell 2008;134:451-460.PMID: 18692468.



35. Abida WM, Gu W. p53-Dependent and p53-independent activation of autophagy by ARF. Cancer Res 2008;68:352-357.PMID: 18199527.



36. Azad MB, Chen Y, Gibson SB. Regulation of autophagy by reactive oxygen species (ROS): implications for cancer progression and treatment. Antioxid Redox Signal 2009;11:777-790.PMID: 18828708.


37. Gilkerson RW, De Vries RL, Lebot P, Wikstrom JD, Torgyekes E, Shirihai OS, et al. Mitochondrial autophagy in cells with mtDNA mutations results from synergistic loss of transmembrane potential and mTORC1 inhibition. Hum Mol Genet 2012;21:978-990.PMID: 22080835.


38. Tanemura M, Saga A, Kawamoto K, Machida T, Deguchi T, Nishida T, et al. Rapamycin induces autophagy in islets: relevance in islet transplantation. Transplant Proc 2009;41:334-338.PMID: 19249550.


39. Lu Z, Luo RZ, Lu Y, Zhang X, Yu Q, Khare S, et al. The tumor suppressor gene ARHI regulates autophagy and tumor dormancy in human ovarian cancer cells. J Clin Invest 2008;118:3917-3929.PMID: 19033662.



40. Nishida K, Yamaguchi O, Otsu K. Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in heart disease. Circ Res 2008;103:343-351.PMID: 18703786.


41. Zhou F, Yang Y, Xing D. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. FEBS J 2011;278:403-413.PMID: 21182587.


42. Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, Tang D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2011;18:571-580.PMID: 21311563.



43. Cui Q, Valentin M, Janumyan Y, Yang E. Bax-/- bak-/- cells exhibit p27 Thr198 phosphorylation and autophagy. Autophagy 2009;5:263-264.PMID: 19139629.


44. Ezaki J, Matsumoto N, Takeda-Ezaki M, Komatsu M, Takahashi K, Hiraoka Y, et al. Liver autophagy contributes to the maintenance of blood glucose and amino acid levels. Autophagy 2011;7:727-736.PMID: 21471734.



45. Xie HJ, Noh JH, Kim JK, Jung KH, Eun JW, Bae HJ, et al. HDAC1 inactivation induces mitotic defect and caspase-independent autophagic cell death in liver cancer. PLoS One 2012;7:e34265PMID: 22496786.



46. Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, Iwata J, Tanida I, et al. Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 2006;441:880-884.PMID: 16625205.


47. Cui D, Wang L, Qi A, Zhou Q, Zhang X, Jiang W. Propofol prevents autophagic cell death following oxygen and glucose deprivation in PC12 cells and cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One 2012;7:e35324PMID: 22509406.



48. Pickford F, Masliah E, Britschgi M, Lucin K, Narasimhan R, Jaeger PA, et al. The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid beta accumulation in mice. J Clin Invest 2008;118:2190-2199.PMID: 18497889.


49. Sciarretta S, Hariharan N, Monden Y, Zablocki D, Sadoshima J. Is autophagy in response to ischemia and reperfusion protective or detrimental for the heart? Pediatr Cardiol 2011;32:275-281.PMID: 21170742.


50. Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M, Sakoda H, Asano T, et al. Distinct roles of autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: roles of AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy. Circ Res 2007;100:914-922.PMID: 17332429.


51. Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, et al. The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature 2004;432:1032-1036.PMID: 15525940.


52. Jaffer S, Shynlova O, Lye S. Mammalian target of rapamycin is activated in association with myometrial proliferation during pregnancy. Endocrinology 2009;150:4672-4680.PMID: 19589861.


53. Kamei T, Jones SR, Chapman BM, KL MC, Dai G, Soares MJ. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway modulates the endocrine differentiation of trophoblast cells. Mol Endocrinol 2002;16:1469-1481.PMID: 12089343.


54. Chifenti B, Locci MT, Lazzeri G, Guagnozzi M, Dinucci D, Chiellini F, et al. Autophagy-related protein LC3 and Beclin-1 in the first trimester of pregnancy. Clin Exp Reprod Med 2013;40:33-37.PMID: 23614114.



55. Signorelli P, Avagliano L, Virgili E, Gagliostro V, Doi P, Braidotti P, et al. Autophagy in term normal human placentas. Placenta 2011;32:482-485.PMID: 21459442.


56. Oh SY, Choi SJ, Kim KH, Cho EY, Kim JH, Roh CR. Autophagy-related proteins, LC3 and Beclin-1, in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Reprod Sci 2008;15:912-920.PMID: 19050324.


57. Crocker IP, Cooper S, Ong SC, Baker PN. Differences in apoptotic susceptibility of cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts in normal pregnancy to those complicated with preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Pathol 2003;162:637-643.PMID: 12547721.



58. Hung TH, Chen SF, Li MJ, Yeh YL, Hsieh TT. Differential effects of concomitant use of vitamins C and E on trophoblast apoptosis and autophagy between normoxia and hypoxia-reoxygenation. PLoS One 2010;5:e12202PMID: 20808946.



59. Hung TH, Hsieh TT, Chen SF, Li MJ, Yeh YL. Autophagy in the human placenta throughout gestation. PLoS One 2013;8:e83475PMID: 24349516.



60. Delorme-Axford E, Bayer A, Sadovsky Y, Coyne CB. Autophagy as a mechanism of antiviral defense at the maternal? fetal interface. Autophagy 2013;9:2173-2174.PMID: 24231730.


61. Chen B, Longtine MS, Nelson DM. Hypoxia induces autophagy in primary human trophoblasts. Endocrinology 2012;153:4946-4954.PMID: 22878401.



62. Choi JH, Lee HJ, Yang TH, Kim GJ. Effects of hypoxia inducible factors-1alpha on autophagy and invasion of trophoblasts. Clin Exp Reprod Med 2012;39:73-80.PMID: 22816073.



63. Yamanaka-Tatematsu M, Nakashima A, Fujita N, Shima T, Yoshimori T, Saito S. Autophagy induced by HIF1alpha overexpression supports trophoblast invasion by supplying cellular energy. PLoS One 2013;8:e76605PMID: 24098539.



64. Hung TH, Chen SF, Lo LM, Li MJ, Yeh YL, Hsieh TT. Increased autophagy in placentas of intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. PLoS One 2012;7:e40957PMID: 22815878.



65. Curtis S, Jones CJ, Garrod A, Hulme CH, Heazell AE. Identification of autophagic vacuoles and regulators of autophagy in villous trophoblast from normal term pregnancies and in fetal growth restriction. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26:339-346.PMID: 23039021.


66. Chen Y, Klionsky DJ. The regulation of autophagy - unanswered questions. J Cell Sci 2011;124:161-170.PMID: 21187343.


67. Smith SC, Baker PN, Symonds EM. Increased placental apoptosis in intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177:1395-1401.PMID: 9423741.


68. Siddiqui IA, Jaleel A, Tamimi W, Al Kadri HM. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2010;282:469-474.PMID: 20549510.


69. Hung TH, Skepper JN, Charnock-Jones DS, Burton GJ. Hypoxia-reoxygenation: a potent inducer of apoptotic changes in the human placenta and possible etiological factor in preeclampsia. Circ Res 2002;90:1274-1281.PMID: 12089065.


70. Chen GQ, Zhang H, Qi HB, Yao ZW, Gao L, Qiu CL. Effects and mechanisms of autophagy of trophoblast cells in severe preeclampsia. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2012;28:294-296.PMID: 22394641.

71. Leung DN, Smith SC, To KF, Sahota DS, Baker PN. Increased placental apoptosis in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;184:1249-1250.PMID: 11349196.


72. Saito S, Nakashima A. Review: The role of autophagy in extravillous trophoblast function under hypoxia. Placenta 2013;34(Suppl): S79-S84.PMID: 23306070.


73. Nakashima A, Yamanaka-Tatematsu M, Fujita N, Koizumi K, Shima T, Yoshida T, et al. Impaired autophagy by soluble endoglin, under physiological hypoxia in early pregnant period, is involved in poor placentation in preeclampsia. Autophagy 2013;9:303-316.PMID: 23321791.



74. Saito S, Nakashima A. A review of the mechanism for poor placentation in early-onset preeclampsia: the role of autophagy in trophoblast invasion and vascular remodeling. J Reprod Immunol 2014;101-102:80-88.PMID: 23969229.


Figure┬Ā1
The processing of autophagy and the roles of autophagy in variable diseases. Membrane fragments form the phagosome, which wraps intracellular materials formed during nucleation. Autophagosome formation is accomplished during the elongation phase. In the maturation process, an autophagosome fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome. Intracellular materials in the phagosome are degraded by lysozymes. Autophagy is involved in variety of diseases (e.g., hepatic, cardiac, and neuronal diseases; cancers; infections; and immune deficiencies) as well as aging through certain mechanisms [11,12].
Figure┬Ā2
Signaling pathway regulation of autophagy by several factors. Autophagy is activated by the MAPK/ERK pathway and the PI3K/AKT pathway. In particular, the mTOR complex is mainly activated by the MAPK/ERK pathway; however, it is inactivated by the accumulation of rapamycin or ROS. During the initiation step, autophagy is triggered by the phosphorylation of the ULK1 kinase complex, which consists of ULK1, Atg3, and Atg17 and is activated by stress signals from the mTOR complex 1 in damaged or dysfunctional cells. The activated mTOR complex phosphorylates ULK1 and Atg13, which represses the ULK1 complex. However, the inactivated mTOR complex dephosphorylates ULK1, which results in self-phosphorylation and activation of the FIP200-Atg13-ULK1 complex, which acts as a node for integrating incoming autophagy signals into autophagosome formation. The activation of the Vps34 complex plays a role in the formation of the isolation membrane and the subsequent nucleation. Therefore, the signaling of autophagy is regulated by ROS or rapamycin, the AMP/ATP ratio, hypoxia, 3-MA, and the combination of Rubicon with the PI3K complex type 3 [17,19]. ROS, reactive oxygen species; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; AKT, protein-serine/threonine kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; AMPK, 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; BNIP3, BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; AMP, 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein; APT, adenosine 5'-triphosphate; 3-MA, 3-methyladenine; UVRAG, UV irradiation resistance-associated gene; ULK1, UNC-51-like kinase 1; FIP200, family interacting protein of 200 kD.
Figure┬Ā3
The intracellular and extracellular factors regulating autophagic signaling. The regulating factors that activate or inactivate the signaling of autophagy are classified as intracellular and extracellular factors. The intracellular autophagic factors involved are nutritional starvation, amino acid concentration, proteasome damage, and damage to other intracellular materials or organelles. The extracellular autophagic factors involved are 3-MA, rapamycin, inositol, and other pathogens [27]. mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Atg, autophagy-related gene; WIM, the Worlds in miniature; 3-MA, 3-methyladenine.
Figure┬Ā4
Effect of hypoxia on the expression of autophagy-associated factors in trophoblasts (HTR-8/SVneo). (A) Cells exposed to hypoxia for 24 hours and 48 hours were analyzed for the expression of phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), phosphoinositide 3-kinase III (PI3K III), Beclin 1, light chain 3 (LC3) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) by western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) The cells were analyzed for the expression of active LC3 by immunofluorescence. A larger view is represented in the right lower corner. Propidium iodide (PI) was used for nuclear staining. Scale bar=80 ┬Ąm. Adapted from Choi et al. Clin Exp Reprod Med 2012;39:73-80 [62].