The protective effect of zinc oxide and selenium oxide nanoparticles on the functional parameters of rat sperm during vitrification
Article information
Abstract
Objective
While sperm freezing (cryopreservation) is an effective method for preserving fertility, it can potentially harm the structure and function of sperm due to an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species. This study aimed to assess the impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) and selenium oxide nanoparticles (SeONPs) on various sperm functional parameters, including motility, plasma membrane integrity (PMI), mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), acrosome membrane integrity (ACi), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels.
Methods
Semen samples were collected from 20 Albino Wistar rats. These samples were then divided into six groups: fresh, cryopreservation control, and groups supplemented with SeONPs (1, 2, 5 µg/mL) and ZnONPs (0.1, 1, 10 µg/mL).
Results
Statistical analysis revealed that all concentrations of SeONPs increased total motility and progressive reduction of MDA levels compared to the cryopreservation control group (p<0.05). However, supplementation with ZnONPs did not affect these parameters (p>0.05). Conversely, supplements of 1 and 2 µg/mL SeONPs and 1 µg/mL ZnONPs contributed to the improvement of PMI and ACi (p<0.05). Yet, no significant change was observed in MMP with any concentration of SeONPs and ZnONPs compared to the cryopreservation control group (p>0.05).
Conclusion
The findings suggest that optimal concentrations of SeONPs may enhance sperm parameters during the freezing process.
Introduction
Freezing is a technique used to preserve fertility in young men with cancer who are candidates for chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as other applicants. This process allows sperm to be stored for an extended period and used in assisted reproductive methods [1]. While sperm freezing can enhance the success of assisted reproductive techniques, it can also damage the sperm's structure and disrupt the vital parameters necessary for successful conception. For instance, the formation of intracellular ice crystals and the increase in solute concentration following this process can be detrimental to sperm, threatening cell survival [2]. The damage resulting from freezing can be associated with the cryopreservation method used.
The vitrification method is an effective technique for sperm freezing, as it prevents the formation of ice crystals [3]. This method is safer, less expensive, and quicker than other sperm freezing methods [4,5]. Regardless of the method used, the sperm freezing process can negatively impact sperm quality due to the excessive production of free oxygen radicals and subsequent oxidative stress. Free radicals produced during the freezing and thawing process can cause oxidative stress. After thawing, these free radicals can disrupt the functional parameters of sperm, such as cell membrane potential, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), motility, viability, and the activity of intracellular enzymes [6].
Spermatozoa are male sex cells that have low cytoplasmic antioxidant content to combat oxidative stress. Therefore, supplementing the freezing environment with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can be effective in preventing oxidative damage and maximizing fertilization success [7-9]. Nanoparticles possess unique biological properties and low toxicity, making them capable of penetrating biological barriers [10,11]. These compounds, which have features such as higher absorption, surface area, surface charge, reactivity, and antioxidant properties, can be used to improve freezing protocols [12].
Zinc is an important element for maintaining reproductive functions such as steroidogenesis, sperm membrane stabilization, acrosome reaction, and the maintenance of chromatin structure, tail structure, and motility. Insufficient zinc consumption can cause oxidative damage to sperm by disrupting antioxidant defense and DNA repair processes [13,14]. Zinc oxide, due to its high zinc content and absorption rate, is the most common form of zinc [15] zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs), with diameters between 1 and 100 nm, are an important product derived from zinc. They have recently been used in extensive animal experiments due to their impact on the reproductive system's performance [16,17]. Selenium is a vital component of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase, which helps reduce free radicals as a cofactor. In the form of selenite, selenium protects cells from oxidative damage with a detoxification effect [18,19]. Studies have shown that selenium oxide nanoparticles (SeONPs) are less toxic than selenite compounds [20]. Recent reports have highlighted positive results from the presence of selenium nanoparticles in sperm freezing extenders of different species on sperm parameters [16,21-23].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of zinc oxide and selenium oxide nanowires on the functional parameters of rat sperm during the vitrification freezing method.
Methods
1. Animals
Sperm samples were collected from 20 adult male Albino Wistar rats, aged 10 to 12 weeks and weighing 150 to 200 g. These animals were supplied by the Garmsar University Laboratory Animal Care Center and maintained under standard conditions. These conditions included a temperature of 22±2 °C, relative humidity of 55%±10%, a light and dark cycle of 12 hours each, and access to nutritious food and clean water. All these measures were in accordance with the regulations required for the care of laboratory animals.
2. SeONP and ZnONP nanoparticles
The zinc and selenium nanoparticles used in this study were 25-nm colloidal particles (Nanozino). These drugs were first dissolved in distilled water, and the solutions were then adjusted to the desired concentrations.
3. Semen collection
To prepare the sperm samples, mice were euthanized using the spinal dislocation method and procedures were conducted under sterile conditions. The epididymal tails, which serve as a storage source for sperm, were isolated and placed in a container filled with 5 mL of hydroxyethyl piperazine ethane sulfonicacid (HEPES) buffer and 3 mL of bovine serum albumin. To facilitate the release of sperm from the tubes containing the epididymal tails, minor scratches were made using a sterile insulin needle. Subsequently, the sample container was transferred to an incubator set at 37 °C with 5% CO2. After 30 minutes, the resulting suspension was decanted into a microtube and maintained at room temperature for subsequent steps [24].
4. Cryopreservation and thawing process
For the freezing procedure, the semen samples were initially separated into six experimental groups. These comprised four groups treated with zinc and selenium nanoparticles, and two control groups (one vitrified and one fresh). The microdroplet method was employed for the freezing process.
In the experimental groups, the sperm suspension was combined with a freezing solution. This solution contained 5% human serum albumin (has; Sigma-Aldrich) and 0.5 mol/L saccharose. This mixture was then diluted with human tubal fluid (HTF; Sigma-Aldrich).
Selenium and zinc nanoparticles were added to the freezing extender of the experimental groups at concentrations of 1, 2, 5 µg/mL and 0.1, 1, 10 µg/mL, respectively. Subsequently, 30 µL/drop of each prepared sample was dispensed onto a metal grid submerged in liquid nitrogen. These samples were then stored in a liquid nitrogen tank for a duration of 2 weeks [25]. Thawing of the samples was achieved by immersing them in 5 mL of pre-heated HTF at a temperature of 37 °C, with the addition of 1% HSA. Following this, the samples were incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 environment and centrifuged for 5 minutes at 500 ×g. Lastly, for evaluation purposes, the resultant pellets were suspended in 50 µL of HTF [26].
5. Evaluation of sperm motility
In this study, we utilized a computer-assisted sperm analyzer (SCA; Microptic Co.) to assess total and progressive motility (PM), as well as dynamic characteristics such as straight-line velocity (VSL), curvilinear velocity (VCL), average path velocity, linearity (LIN), and beat cross frequency (BCF). Initially, we placed the Mackler chamber slide on a warm stage set at a temperature of 37 °C for a duration of 30 minutes. Subsequently, we applied 10 µL of sperm suspension onto the slide and covered it. Finally, we randomly evaluated 500 sperm from five different microscopic fields.
6. Evaluation of plasma membrane integrity
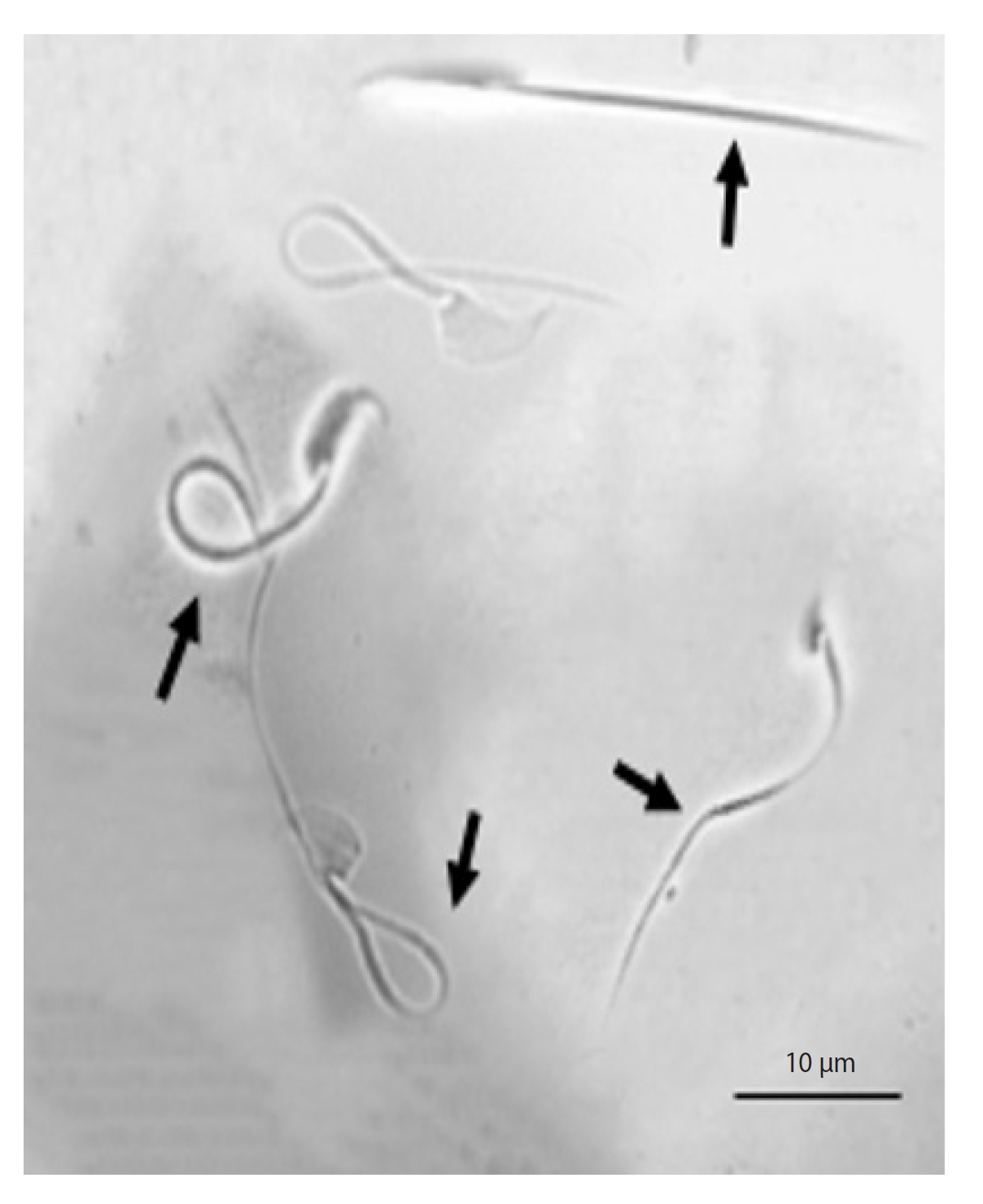
For this evaluation, we utilized the hypo-osmotic swelling (HOS) test. This test is predicated on the osmolarity of the environment in which the sperm is situated. The HOS test medium comprises 0.9 g of fructose, 0.49 g of sodium citrate, and 100 mL of distilled water. These components create a hypo-osmotic environment for the sperm by establishing an osmolarity of 100 mOsmol/kg. Following dissolution, the samples underwent centrifugation (1,200 ×g, 10 minutes). Subsequently, the supernatant solution was isolated, and 20 µL of the centrifuged suspension was introduced to 200 µL of the HOS test environment and incubated for 30 minutes. Afterward, 10 µL of each sample was extracted and affixed to a slide. On each slide, 200 sperm were selected and scrutinized across approximately three microscopic fields using a phase-contrast microscope. Sperm with coiled tails were identified as having integrated membranes, while sperm with uncoiled tails were classified as having non-integrated membranes (Figure 1) [27].
7. Evaluation of mitochondrial membrane potential
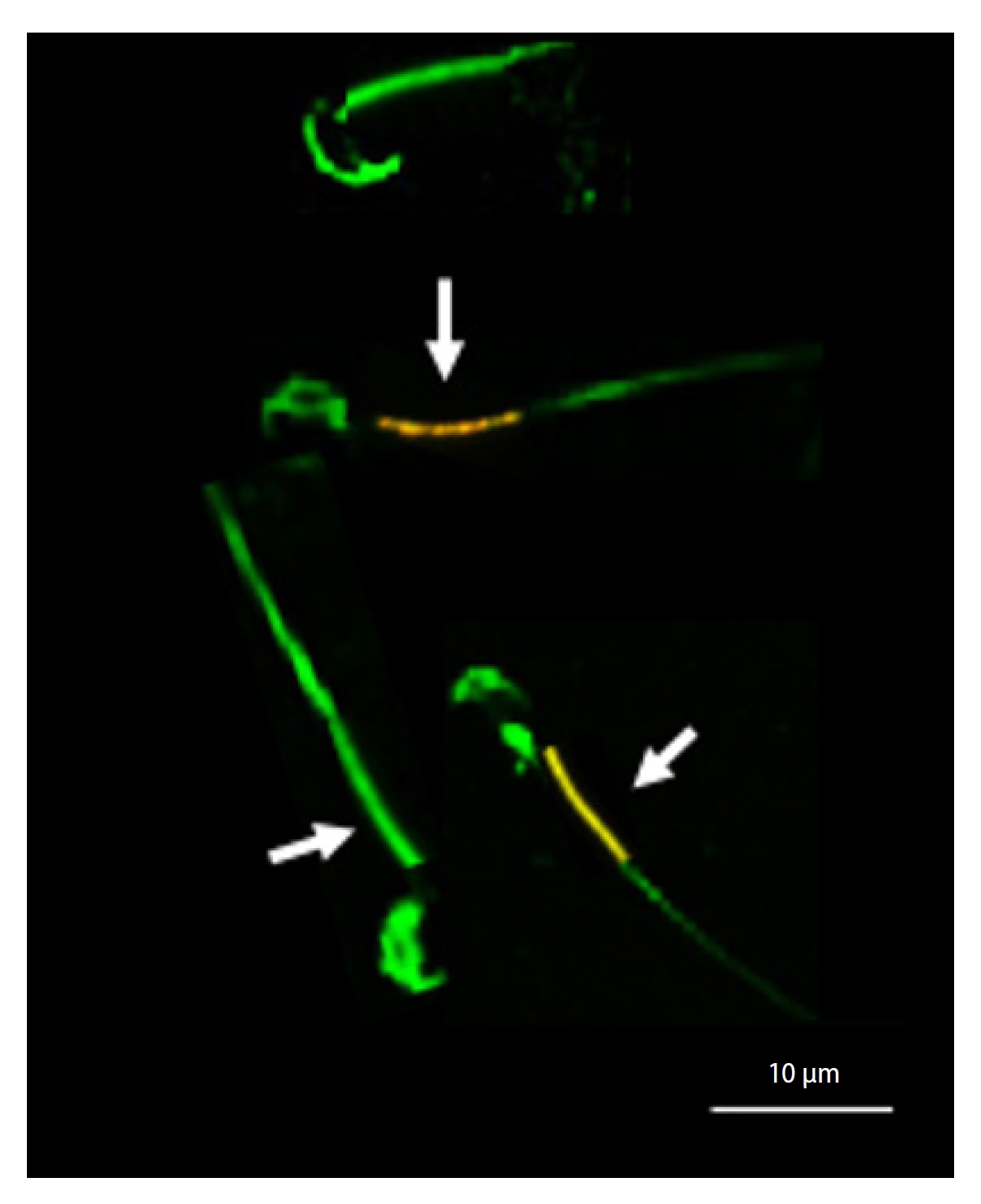
To evaluate MMP, we employed the lipophilic cationic fluorochrome (JC-1) method. Initially, we diluted 10 µL of the sperm suspension in 30 µL of Tris buffer, followed by staining with 0.5 µL of JC-1. Post incubation at room temperature, we examined 200 sperm under an epifluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss) at ×400 magnification across three microscopic fields, using bandpass (BP) 450 to 490 nm restriction and longpass (LP) 515 nm emission filters. Our observations revealed an orange color in the mid-section of sperm with high MMP, and a green color in the mid-section of sperm with low MMP (Figure 2) [28].
8. Evaluation of malondialdehyde concentration
The concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA) was assessed using the TB reaction and a spectrophotometer (UV-1200; Shimadzu). In this procedure, 1 mL of cold trichloroacetic acid 20% (w/v) was added to 1 mL of sperm suspension to precipitate the protein. Following centrifugation (950 g, 15 minutes), 1 mL of thiobarbituric acid 0.67% (w/v) was introduced to the supernatant and incubated for 10 minutes at 100 °C using the bain-marie method. After the mixture had cooled, the final result was determined as mol/mL at a wavelength of 532 nm, using a spectrophotometer [29].
9. Evaluation of acrosome integrity
In this evaluation, a prepared smear, consisting of 10 µL of sperm suspension, was stained with 30 µL of fluorescein isothiocyanate-peanut agglutinin (FITC-PNA) and then refrigerated for 15 minutes. Following this, it was immersed twice in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and allowed to dry at room temperature. Subsequently, 5 µL of Uniform Closing Dataset (UCD) solution, which contained 0.5 mL of PBS, 5 mg of p-phenylenediamine, and 4.5 mL of glycerol, was applied to the slide and covered with a coverslip. A total of 200 sperm were then examined under an epifluorescence microscope at ×400 magnification, using a BP 450 to 490 nm excitation filter and LP emission 515 nm. Sperm observed to have green acrosomes were classified as having intact acrosomes, while those with colorless acrosomes or only green equatorial regions were considered to have damaged acrosomes (Figure 3) [30].
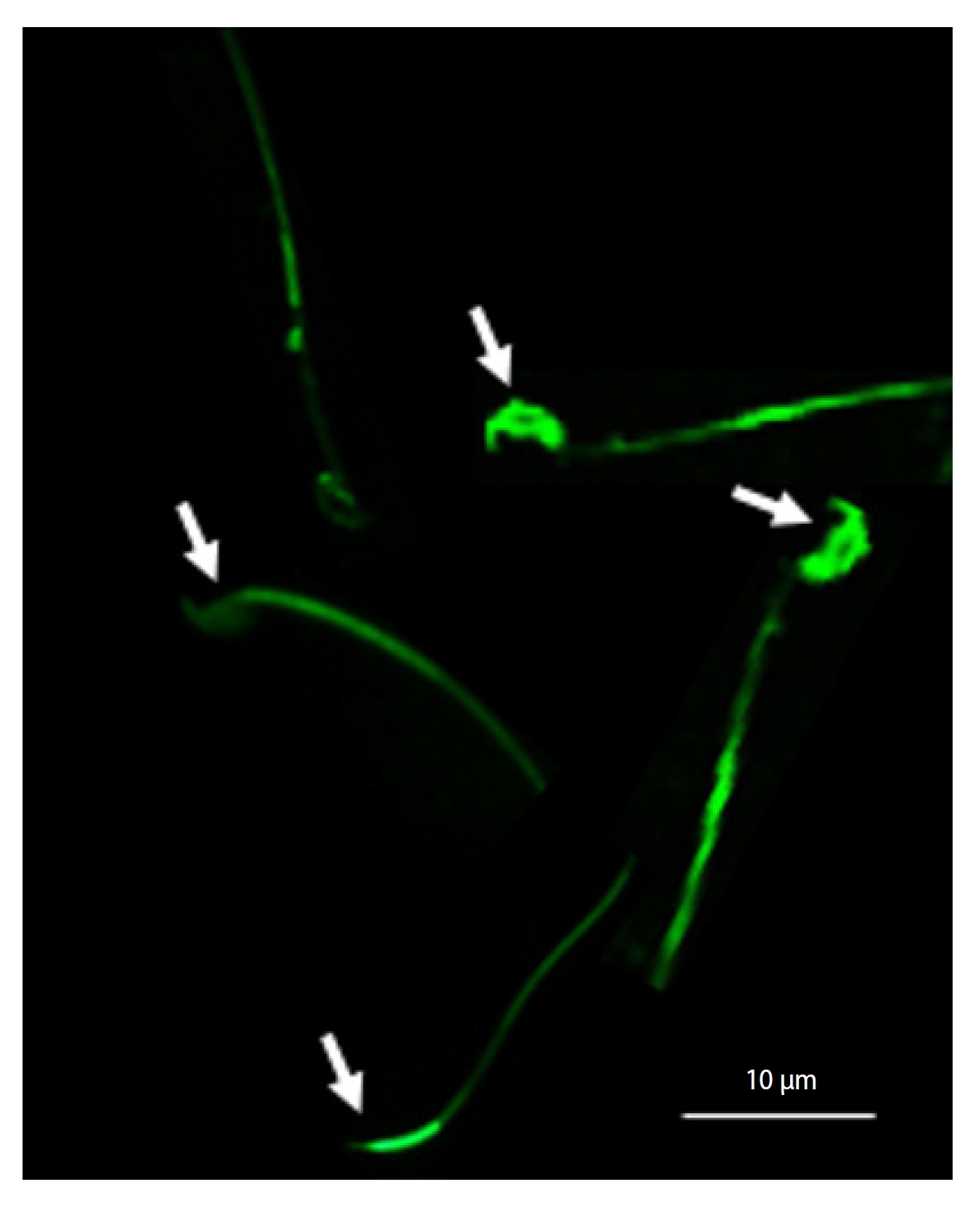
Evaluation of acrosome integrity using fluorescein isothiocyanate-peanut agglutinin (FITC-PNA) staining. Sperm with green acrosomes were considered to have intact acrosomes, while sperm with colorless acrosomes or with only green equatorial regions were considered to have damaged acrosomes (arrows).
10. Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 20 (IBM Corp.). The tests used in this study were as follows: the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and the post hoc Tukey range test. The results were expressed as mean±standard error. The significance level was set at p≤0.05.
11. Ethical statement
This study was approved by the research ethics committee with laboratory animals of Garmsar Azad University (723-16A11).
Results
Table 1 compares the effects of SeONPs and ZnONPs on the motility, PM, and dynamic characteristics of rat sperm. The results indicate that the addition of SeONPs (at all three concentrations) to the freezing extender significantly improved both total motility (TM) and PM compared to the vitrified group (p<0.05). In contrast, the ZnONPs supplement did not significantly affect TM and PM at any concentration (p>0.05). Furthermore, neither SeONPs nor ZnONPs had any impact on dynamic characteristics (VCL, VSL, LIN, and BCF) (p>0.05).
As shown in Table 2, there was a significant increase in the percentage of plasma membrane integrity (PMI) and acrosome membrane integrity (ACi) in the groups treated with SeONPs at concentrations of 1 and 2 µg/mL, as well as in the group treated with ZnONPs at a concentration of 1 µg/mL, compared to the vitrified group (p<0.05).
At all six concentrations, the inclusion of SnONPs and ZnONPs in the rat sperm freezing extender did not enhance MMP (p>0.05). The MDA concentration was significantly higher in the groups with 1 µg/mL ZnONPs and 1, 2, and 5 µg/mL SeONPs compared to the vitrified group (p<0.05).
Discussion
In recent years, numerous comprehensive studies have been undertaken to verify that the process of freezing sperm can inflict structural and functional damage on these cells. Physiological studies have indicated that one of the most detrimental factors in the freezing process is the generation of oxidative stress, caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Sperm cells lack the capacity to fully counteract the damage caused by freezing due to an ineffective antioxidant system [30]. Therefore, recent research has concentrated on the impact of incorporating various antioxidants into sperm freezing extenders to rectify this deficiency. In this study, we utilized potent antioxidants, selenium and zinc nanowires, to induce an antioxidant effect. Both zinc and selenium are crucial elements in the process of spermatogenesis and maturation. Selenium is a key component of glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme that aids in preserving sperm by eliminating ROS and thereby safeguarding the cell membrane [31]. Additionally, the presence of zinc in seminal plasma assists in maintaining the sperm membrane and nucleus [32].
Our results showed that the presence of SeONPs in the sperm freezing extender significantly enhances motility. This aspect of the result aligns with the findings of other researchers who assessed the impact of adding selenium in concentrations of 1, 2, 5 µg/mL and 1 mM on sperm motility [9,24,33]. These results are likely attributable to the role of Se in the oxidative phosphorylation activity of mitochondria, and since sperm motility is associated with mitochondria, this parameter improved [34]. However, while it was anticipated that Zn would enhance sperm motility, given its crucial role in regulating phosphorylation and influencing motility through adenosine triphosphate production, this was not observed. The reason for this could potentially be attributed to an inadequate concentration. The addition of ZnONPs to the freezing environment did not impact the dynamic characteristics of sperm. These findings align with the reports of some researchers [35,36], but contradict the results of others [37]. This discrepancy could be related to the different types and concentrations used.
The cell membrane, by preserving the structure within the cell, plays a vital role in defending against osmotic changes and ionic imbalance caused by freezing. If the cell structure is damaged, sperm homeostasis is disrupted and the cell fails to function properly. PMI showed significant improvements in the 1 and 2 µg/mL SeONPs and 1 µg/mL ZnONPs groups, compared to the vitrified group. A study conducted by Safa et al. [38] and Shahin et al. [16] on the effect of adding 1 µg/mL and 1% selenium, respectively, on sperm parameters, demonstrated that this concentration increased viability and PMI in the experimental group. These results also align with the findings of Farhadi et al. [35] and Arruda et al. [39], who stated that the addition of concentrations of 0.1, 1, 10 µg/mL and 10, 50, 100, 200 µg/mL of ZnONPs to the sperm freezing extender did not significantly improve PMI, compared to the control group. The differing results of the two elements (selenium and zinc) can be explained by the fact that selenium functions powerfully as an antioxidant to reduce lipid peroxidation and maintain osmotic or even pH balance.
Another parameter evaluated in this study was ACi. The groups containing 1 and 2 µg/mL SnONPs and 1 µg/mL ZnONPs exhibited a higher percentage of intact acrosomes. These results are consistent with the findings of Farhadi et al. [35] and Nateq et al. [22], but contrast with the results of Arruda et al. [39]. Our study indicated that the optimal concentration required to improve this parameter was 1 µg/mL zinc and 1.2 µg/mL selenium, and that increasing the concentration reduced the percentage of intact acrosome. At high doses, this result is likely related to the peroxidation effects of antioxidants and the associated toxic effects [40]. The MMP did not exhibit a significant effect at any of the used concentrations of selenium and zinc. The sperm membrane contains a high concentration of unsaturated fatty acids, so protecting sperm against peroxidation damage necessitates an effective antioxidant system. MDA is regarded as an indicator of lipid peroxidation under stressful conditions [41].
The findings of this study indicate that SeONPs led to a reduction in MDA levels across all concentrations. This decrease in MDA levels, which is linked to a reduction in lipid peroxidation, can enhance sperm parameters, including motility, under oxidative stress conditions. This could potentially explain the observed improvement in total mobility among groups receiving SeONPs at optimal concentrations. This outcome aligns with the findings of other researchers [21]. However, in studies involving ZnONPs, no significant decrease in MDA levels was observed. Our results corroborate that high MDA levels in semen are associated with poor sperm motility. It was noted that the concentrations of ZnONPs used did not possess the capacity to reduce MDA levels and, consequently, lipid peroxidation, ultimately failing to enhance sperm mobility.
In conclusion, the results of this study indicate that selenium nanoparticles, at concentrations of 1 and 2 µg/mL, significantly enhance sperm parameters, suggesting an optimal concentration. In contrast, zinc nanoparticles appear to have negligible impact on these parameters. Selenium nanoparticles are shown to boost sperm motility by markedly reducing MDA levels. The beneficial outcomes of SeONPs may be due to their superior access to the antioxidant system and their capacity to neutralize more free radicals. Owing to their structural characteristics, these particles have an expanded capacity to eliminate ROS. It is advisable to carry out further research on various species and across a broader range of concentrations to confirm the influence of nanoparticles on sperm parameters during the freezing process.
Notes
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: NTS, TMG. Data curation: ZH, MSN. Formal analysis: NGB, SSZ. Methodology: TMG. Project administration: NTS. Visualization: ZH, NGB. Writing-original draft: MSN, SSZ. Writing-review & editing: TMG.