Optimal numbers of mature oocytes to produce at least one or multiple top-quality day-3 embryos in normal responders
Article information
Abstract
Objective
We attempted to identify the optimal cutoff numbers of mature oocytes that would produce at least one or multiple top-quality (grade A) day-3 embryos in normal responders undergoing stimulated in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles.
Methods
We selected 210 fresh IVF cycles performed in 170 infertile women at a single center from January 2014 to November 2019. Four to 14 (total) oocytes were obtained in all cycles after conventional ovarian stimulation. A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to find the moderate and extreme cutoff numbers of mature oocytes that would produce ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos.
Results
The cutoff number of mature oocytes was significantly correlated with the number of top-quality embryos (r = 0.467, p= 0.000). The moderate cutoff number of mature oocytes was ≥ 3, ≥ 5, ≥ 5, ≥ 6, and ≥ 6 for obtaining ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos, respectively. The extreme cutoff number of mature oocytes was ≥ 9, ≥ 9, ≥ 10, ≥ 10, and ≥ 11 for obtaining ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos, respectively.
Conclusion
We present the optimal cutoff numbers of mature oocytes that would yield ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos with 95% specificity. Our findings could help infertility clinicians to set target mature oocyte numbers in women undergoing stimulated IVF cycles.
Introduction
In in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles, the pregnancy rate depends on the number of embryos transferred [1-3]. More specifically, the pregnancy rate after IVF depends on the number of good-quality embryos transferred [4-7]. Volpes et al. [8] reported that the number of good-quality embryos available on day 3 was a strong predictor of both the pregnancy rate and the implantation rate. In their study, when more than three good-quality embryos were available, the overall pregnancy rate was 64.3%, whereas it was only 39.5% when three good-quality embryos were available [8]. In a meta-analysis, the total number of good-quality embryos was found to be the most important predictor of the clinical pregnancy rate after IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) among 27 candidate variables [9]. Terriou et al. [7] demonstrated that the mean score of transferred embryos was a better predictor of pregnancy than the number of transferred embryos itself and/or the age of the woman undergoing IVF. Lee et al. [10] also suggested that the score of the three best embryos on day 3 was more closely correlated with the pregnancy rate after IVF than the number of good-quality embryos or the total embryo score.
Recently, the oocyte number has been reported to be closely related with the pregnancy rate after IVF. Sunkara et al. [11] found that the best chance of live birth was seen with approximately 15 oocytes. Magnusson et al. [12] reported that the live birth rate increased up to 11 oocytes and plateaued after that number. Steward et al. [13] showed that the highest pregnancy rate (30.8%) was found when between 11 and 15 mature oocytes were available for ICSI. Considering the above reports, the primary goal in stimulated IVF cycles is to obtain one or multiple good-quality embryos, and for that goal, the retrieval of multiple oocytes may be an important prerequisite. While a high number of oocytes clearly is a strong predictor of multiple good-quality embryos; however, the specific number of oocytes needed to obtain one or multiple good-quality embryos has not been established.
In this study, we attempted to identify the specific cutoff numbers of mature oocytes that would be appropriate for obtaining at least 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 top-quality embryos in normal responders undergoing stimulated IVF cycles.
Methods
1. Study subjects
We retrospectively selected 210 stimulated IVF/ICSI cycles from January 2014 to November 2019 among patients treated at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. Cycles in which 4 to 14 total oocytes were retrieved after conventional ovarian stimulation were included in the analysis. The indications for IVF/ICSI were unexplained infertility (52 cycles), tubal factor infertility (39 cycles), decreased ovarian response (38 cycles), male factor infertility (23 cycles), endometriosis (11 cycles), ovulation factor infertility (9 cycles), uterine/endometrial factor infertility (9 cycles), and mixed causes (29 cycles). The Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital approved our study (IRB No. B 1910-571-107).
2. Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation protocols
A flexible gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist protocol was used in all IVF/ICSI cycles. Gonadotropins were started on day 3 of the menstrual cycle and the doses were adjusted according to individual ovarian response. When the leading follicle reached a diameter of 14 mm, 0.25 mg/d of cetrorelix (Cetrotide; Merck Serono, Darmstadt, Germany) was started. When the leading follicle(s) reached a diameter of 18 mm, 250 µg or 500 µg of recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG; Ovidrel, Merck-Serono; 194 cycles), a GnRH agonist (Decapeptyl 0.2 mg, Ferring, Germany; 4 cycles) or 250 µg of recombinant hCG+a GnRH agonist (Decapeptyl 0.2 mg; 12 cycles) was administered, and oocytes were retrieved 35–36 hours later.
After collection of cumulus-oocyte complexes (COC), the maturity of oocytes was assessed according to the presence or absence of a germinal vesicle (GV) or the first polar body (PB) by stereomicroscopy. In most cases, oocyte maturity could be easily evaluated under stereomicroscopy on the basis of the cumulus pattern. In situations where the maturity was unclear due to a dark COC or blood clots, the oocytes were denuded using 85 IU/mL hyaluronidase (Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA) and mechanical pipetting. Immature oocytes were identified by the absence of the first PB and then classified as GVstage or metaphase I (MI)-stage depending on the presence of a visible GV. Culture of GV- and/or MI-stage oocytes was carried out in maturation medium (Global Total; Life Global, Airdropped, Denmark) supplemented with recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone (75 mIU/mL, Merck-Serono) and recombinant hCG (0.5 IU/mL, Merck-Serono). The culture of all oocytes continued in 1 mL of maturation medium for up to 48 hours in an incubator (Mini Incubator; Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA) with a triple-gas system (6% CO2, 5% O2, 89% N2 with high humidity).
Oocytes were then fertilized by the conventional method (77 cycles), ICSI (115 cycles), or half ICSI (18 cycles). The indications for ICSI were as previously described: (1) severe male factor infertility; (2) a ≤ 20% fertilization rate in a prior conventional insemination cycle; (3) repeated implantation failure ( ≥ 3 times); (4) advanced maternal age ( ≥ 40 years); (5) presence of endometrioma on the day of oocyte retrieval; or (6) poor-quality oocytes that included blood clots attached to the cumulus oophorus at the time of retrieval [14]. Normal fertilization was confirmed when two distinct pronuclei and a second PB were present. The fertilized oocytes were cultured in the culture medium (Global Total; LifeGlobal, Guilford, CT, USA) in an incubator with a triple-gas system.
3. Embryo quality assessment
Embryo quality was assessed at day 3 after insemination using the following morphological grading system: grade A, equal-sized blastomeres without fragments or apparent morphological abnormalities; grade B, equal-sized blastomeres and < 20% of fragments without apparent morphological abnormalities; grade C, irregularity of blastomeres and 20% to 50% of fragments without apparent morphological abnormalities; grade D, irregularity of blastomeres and > 50% fragments with apparent morphological abnormalities [15]. In the present study, grade A embryos were regarded as top-quality embryos.
4. Data analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS ver. 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Pearson correlation analysis was performed to elucidate which variables were associated with the number of topquality embryos. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to determine the cutoff numbers of mature oocytes that would produce ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos. The cutoff point using the Youden index was defined as the moderate cutoff. We also obtained the extreme cutoff values following the methodology that we used in a previous study [16]. To maximize the specificity (true negative rate), the extreme cutoff value was selected by establishing a false positive rate of 5% (i.e., a specificity of 95%). A p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
The demographic characteristics and cycle outcome parameters of all study subjects are shown in Table 1. Pearson correlation coefficients are presented in Table 2. The number of mature oocytes showed a significant correlation with the number of top-quality embryos (r= 0.467, p= 0.000). A regression line depicting the association between the number of mature oocytes and the number of top-quality embryos is shown in Figure 1. At least one top-quality embryo was obtained in 163 cycles, at least two top-quality embryos were obtained in 106 cycles, at least three top-quality embryos were obtained in 65 cycles, at least four top-quality embryos were obtained in 36 cycles, and at least five top-quality embryos were obtained in 18 cycles.
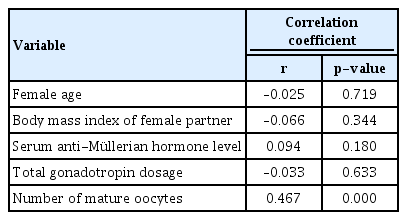
Pearson correlation coefficients for the associations between the number of top-quality (grade A) embryos and other factors
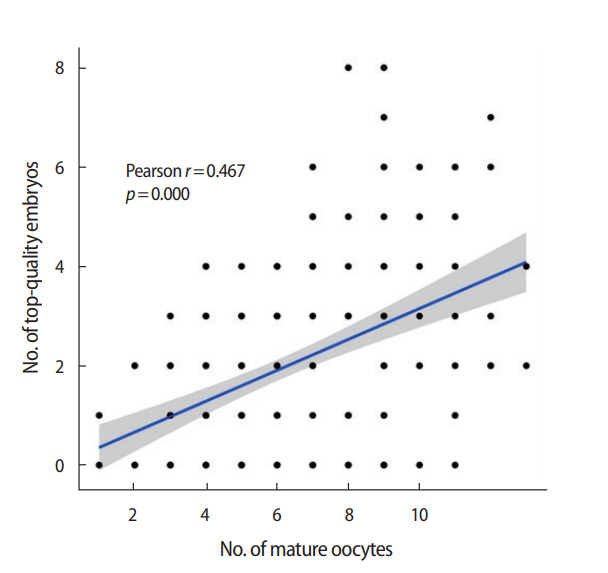
Matrix scatter plot and regression line showing the correlation between the number of mature oocytes and the number of topquality (grade A) embryos (r= 0.467, p= 0.000).
As shown in Table 3, the moderate cutoff numbers of mature oocytes were ≥ 3, ≥ 5, ≥ 5, ≥ 6, and ≥ 6 for obtaining ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos, respectively. The extreme cutoff numbers of mature oocytes were ≥ 9, ≥ 9, ≥ 10, ≥ 10, and ≥ 11 for obtaining ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos, respectively. Receiver operating curve analysis showing the cutoff numbers of mature oocytes needed to obtain ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, or ≥ 5 top-quality embryos are depicted in Figure 2. When there were ≥ 9 mature oocytes (44 cycles), the mean number of top-quality embryos was 3.3 ± 2.2, at least one top-quality embryo was obtained in 86.4% of the cycles, and at least two top-quality embryos were obtained in 79.5% of the cycles. When there were ≥ 10 mature oocytes (23 cycles), the mean number of top-quality embryos was 3.5 ± 2.1, at least three top-quality embryos were obtained in 60.9% of the cycles, and at least four top-quality embryos were obtained in 47.8% of the cycles. When there were ≥ 11 mature oocytes (15 cycles), the mean number of top-quality embryo was 3.5 ± 2.2, and at least five topquality embryos were obtained in 33.3% of the cycles.
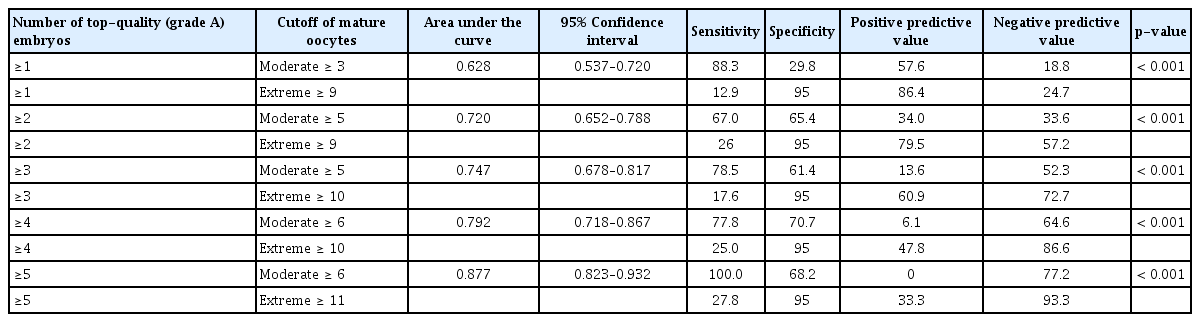
Cutoff numbers of mature oocytes needed to obtain ≥1, ≥2, ≥3, ≥4, or ≥5 top-quality (grade A) embryos
Discussion
In the present study, we found that the presence of ≥ 9, ≥ 10, and ≥ 11 mature oocytes strongly predicted the ability to produce ≥ 1–2, ≥ 3–4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos, respectively, with a high probability. In most fresh IVF cycles, obtaining ≥ 1–2 top-quality embryos may be ideal; thus, for this purpose, obtaining ≥ 9 mature oocytes is recommended. When there were ≤ 8 mature oocytes in the present study, the mean number of top-quality embryos was 1.6 ± 1.4 (166 cycles). In contrast, when there were ≥ 9 mature oocytes (44 cycles), the mean number of top-quality embryos was 3.3 ± 2.2.
Some investigators have reported that the live birth rate depends on the number of oocytes [11-13]. Retrieving more oocytes could result in more available good-quality embryos, which would lead to higher pregnancy and live birth rates. Cai et al. [17] suggested that the number of oocytes can be considered as a surrogate of embryo quality because an abundant number of oocytes predicts a larger pool of available embryos and a higher possibility of obtaining one or two good-quality embryos.
In the present study, the number of top-quality embryos was correlated with the number of mature oocytes. Female age, body mass index, serum anti-Müllerian hormone levels, and total gonadotropin dosage were not related with the number of top-quality embryos. Hsu et al. similarly reported that the number of total oocytes had a positive correlation with the number of good-quality embryos (r= 0.329, p< 0.001) [18]. They also showed that the number of oocytes was positively correlated with pregnancy and implantation rates. A recent meta-analysis demonstrated that the number of total oocytes had strong positive associations with the presence of top- or good-quality day-2, day-3, day-5, and day-6 embryos [19]. In IVF cycles, it is important to obtain at least one good-quality embryo, but the quality of surplus embryos from the same oocyte retrieval cohort is also important. Surplus embryos could be cryopreserved and used later, thereby maximizing the overall pregnancy rate from the same oocyte retrieval cohort.
A limitation of our study is that we only included normal responders. If the study had included poor responders and/or high responders, the cutoff number of mature oocytes needed to produce at least one or multiple top-quality embryos would have been different. We did not consider the pregnancy rate, so we could not analyze the cutoff number of mature oocytes needed to optimize the likelihood of establishing clinical pregnancy. A further large-scale study would be needed to determine the associations among mature oocyte number, the number of top-quality embryos, the clinical pregnancy rate, and the live birth rate. In conclusion, we demonstrated that the extreme cutoff numbers of mature oocytes were ≥ 9, ≥ 9, ≥ 10, ≥ 10, and ≥ 11 for obtaining ≥ 1, ≥ 2, ≥ 3, ≥ 4, and ≥ 5 top-quality embryos, respectively. We included normal responders only; however, our findings could help infertility clinicians to set target mature oocyte numbers in women undergoing stimulated IVF cycles.
Notes
Conflict of interest
Byung Chul Jee has been an editor of Journal of Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine since 2018; however, he was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing–original draft, review & editing: all authors.